Diagnosis Definition
- AD is a heterogeneous spectrum of neurodegenerative diseases associated with abnormal amyloid accumulation in the brain; the etiology is unknown
- Histologic features of AD include extracellular amyloid plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles
- AD is the most common cause of both late-onset and early-onset dementia; approximately ⅓ of persons over age 85 meet the criteria for AD and the prevalence approaches 50% over age 95
- The most common AD syndrome presents with memory deficits
Imaging Findings
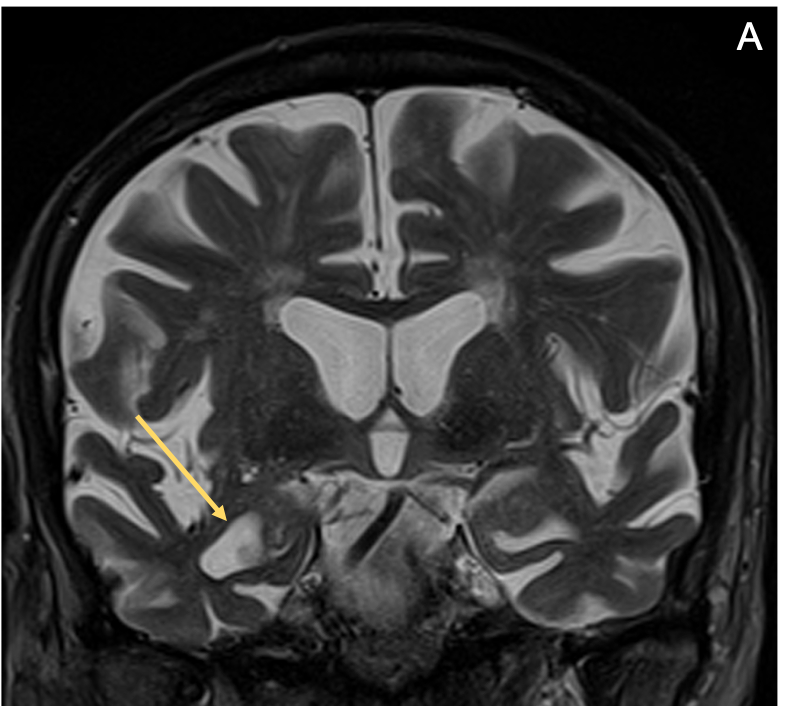
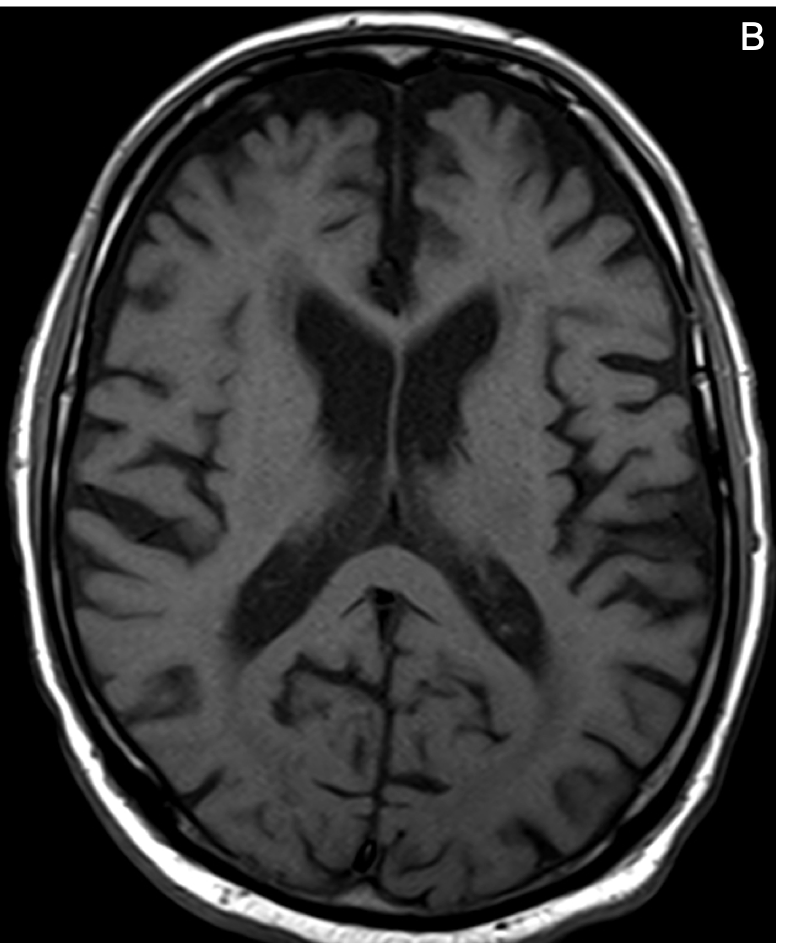
- MRI is considered the preferred neuroimaging examination for AD because it allows for accurate measurement of the 3-dimensional volume of brain structures, especially the size of the hippocampus
- The most common MRI finding of AD is atrophy of the medial temporal lobes, particularly the hippocampi, followed by atrophy of the paralimbic and association neocortex of the temporal and parietal lobes
- A typical AD pattern is hippocampal atrophy that is disproportionately greater than diffuse brain parenchymal volume loss
Pearls
- FDG-PET is very useful for the evaluation of AD and can show extensive abnormalities even when MRI shows little or no atrophy; however, amyloid PET should not be performed as a screening examination in cognitively normal patients, as a substantial proportion of older patients have a significant burden of cerebral amyloid and yet may not develop AD
- Neuroimaging can also used to exclude other causes of dementia, such as normal-pressure hydrocephalus, brain tumors, subdural hematoma, and multiple infarctions
References
- Nasrallah IM, Wolk DA. Multimodality imaging of Alzheimer disease and other neurodegenerative dementias. J Nucl Med 2014; 55(12):2003-2011
- Petersen RC, Stevens JC, Ganguli M,Tangalos EG, Cummings JL, DeKosky ST. Practice parameter: early detection of dementia: mild cognitive impairment (an evidence-based review). Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2001: 56(9):133-1142
Case-based learning.
Perfected.
Learn from world renowned radiologists anytime, anywhere and practice on real, high-yield cases with Medality membership.
- 100+ Mastery Series video courses
- 4,000+ High-yield cases with fully scrollable DICOMs
- 500+ Expert case reviews
- Unlimited CME & CPD hours