Diagnosis Definition
- “Coronavirus Disease 2019” (COVID-19) is a disease caused by the “SARS-CoV2” virus, a novel coronavirus that was first reported in December 2019 in Wuhan, China
- The real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test for COVID-19 has high specificity but relatively low sensitivity (60%–70%)
- Most patients with lower respiratory tract infection caused by COVID-19 present with fever, cough, dyspnea, and myalgia; up to 29% of patients have acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
- The Society of Thoracic Radiology (STR) does not recommend routine CT screening for the diagnosis of patients under investigation for COVID-19; chest CT can be restricted to patients who test positive for COVID-19 and who are suspected of having complicating features such as abscess or empyema
Imaging Findings
- Up to 50% of patients with COVID-19 infection may have normal CT scans within 0–2 days after onset of symptoms and patients with COVID-19 pneumonia may have lung abnormalities on chest CT but an initially negative RT-PCR
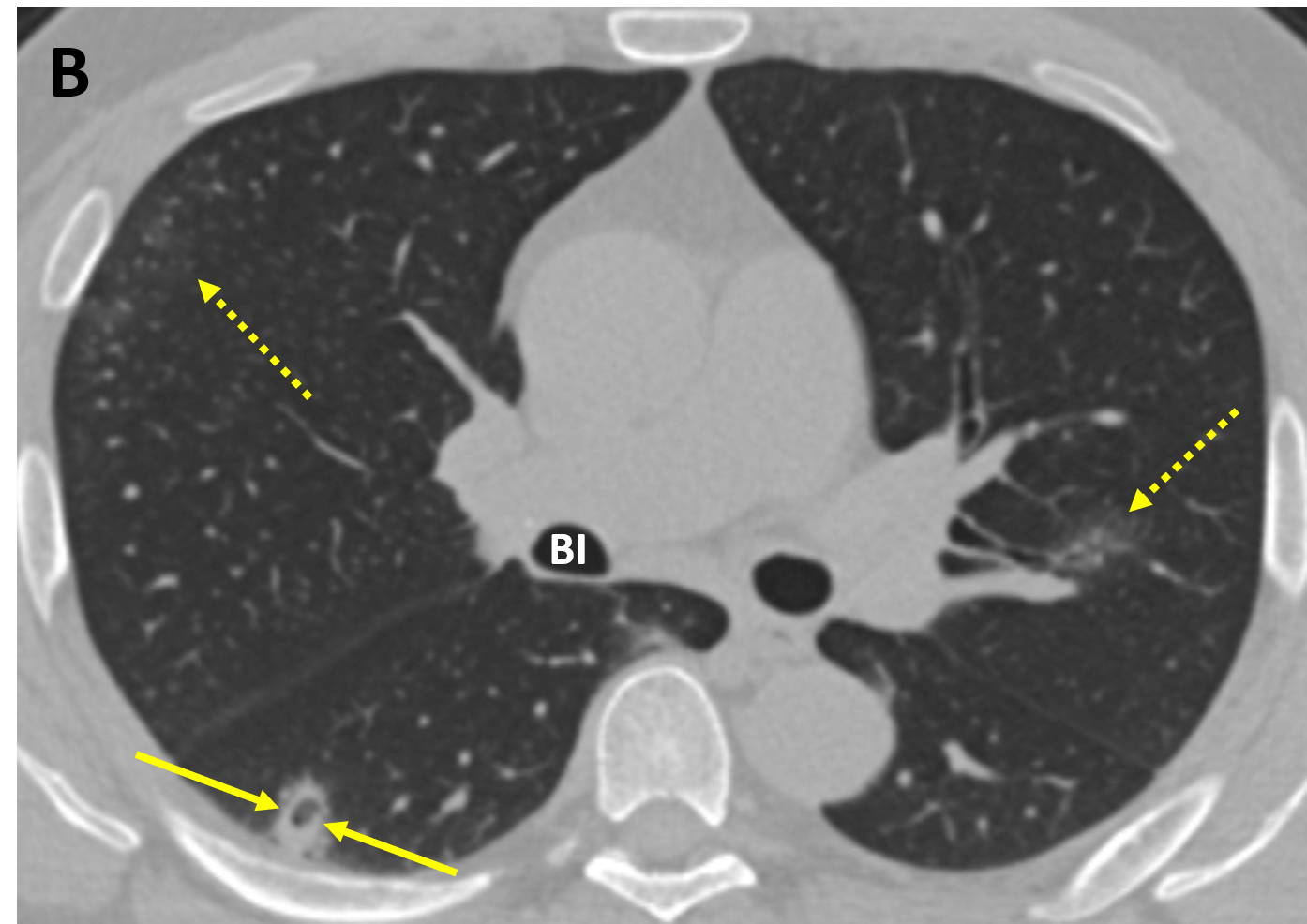
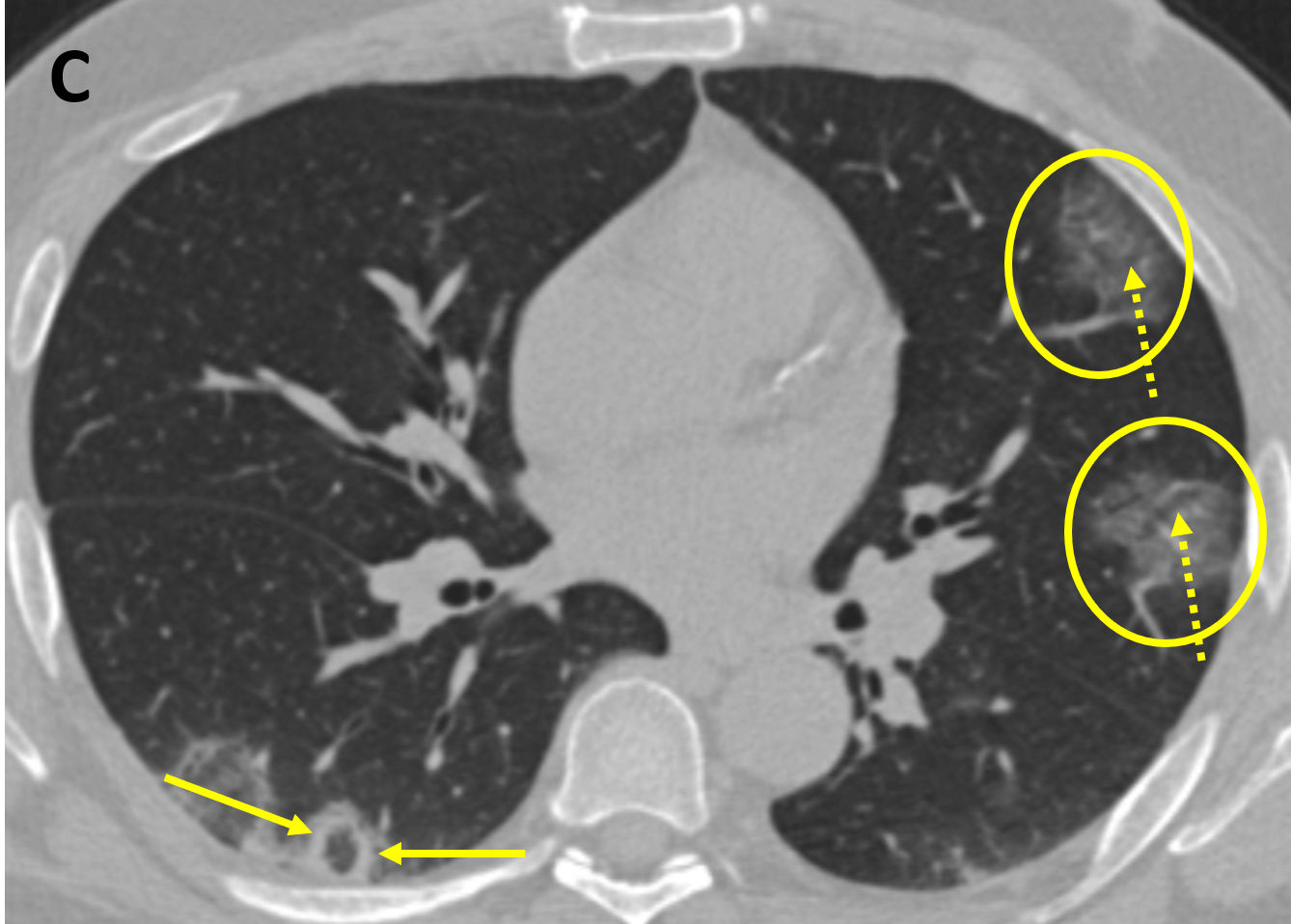
- Typical early lung abnormalities seen on CT are bilateral, peripheral, round, predominantly lower lung ground glass opacities (opacities that do not obscure underlying vessels and airways); the features are typical of an organizing pneumonia pattern of lung injury
- As disease progresses, crazy paving (ground-glass opacities associated with thickened interlobular septae and intralobular lines) and consolidation become the dominant CT findings, peaking around 9-13 days, followed by slow clearing at approximately one month and beyond (the typical evolution of acute lung injury)
- In some cases, a reversed halo/atoll sign is seen, which is rounded or crescentic ground-glass opacity surrounded by consolidation
Pearls
- Pleural effusion, extensive tiny lung nodules, and lymphadenopathy occur in a very small number of cases and suggest bacterial superinfection or another diagnosis
- Although bilateral disease is most typical, unilateral findings do not rule out COVID-19, especially in the early stage
References
- Chung M, Bernheim A, Mei X, Zhang N, Huang M, et al. CT Imaging Features of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Radiology. Published online February 4, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020200230
- Kanne JP, Little BP, Chung JH, Elicker BM, Ketai LH. Essentials for Radiologists on COVID-19: An Update—Radiology Scientific Expert Panel. Radiology. Published online February 27, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020200527
- Society of Thoracic Radiology (STR) Position Statement March 10, 2020. https://veritastv.org/programs/covid-19
Case-based learning.
Perfected.
Learn from world renowned radiologists anytime, anywhere and practice on real, high-yield cases with Medality membership.
- 100+ Mastery Series video courses
- 4,000+ High-yield cases with fully scrollable DICOMs
- 500+ Expert case reviews
- Unlimited CME & CPD hours