Diagnosis Definition
- Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) can be intracerebral (within the brain) and extracerebral (e.g., subarachnoid, subdural, and epidural)
- The most common cause of ICH between ages 45 and 70 is hypertensive hemorrhage
- Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) is also an important cause of spontaneous ICH in the elderly
- Tumors with a propensity to bleed include glioblastoma multiforme and vascular metastatic lesions including melanoma, thyroid carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, and choriocarcinoma
- Other common causes of ICH are coagulopathy, trauma, vascular malformations, vasculitis and hemorrhagic infarction
Imaging Findings
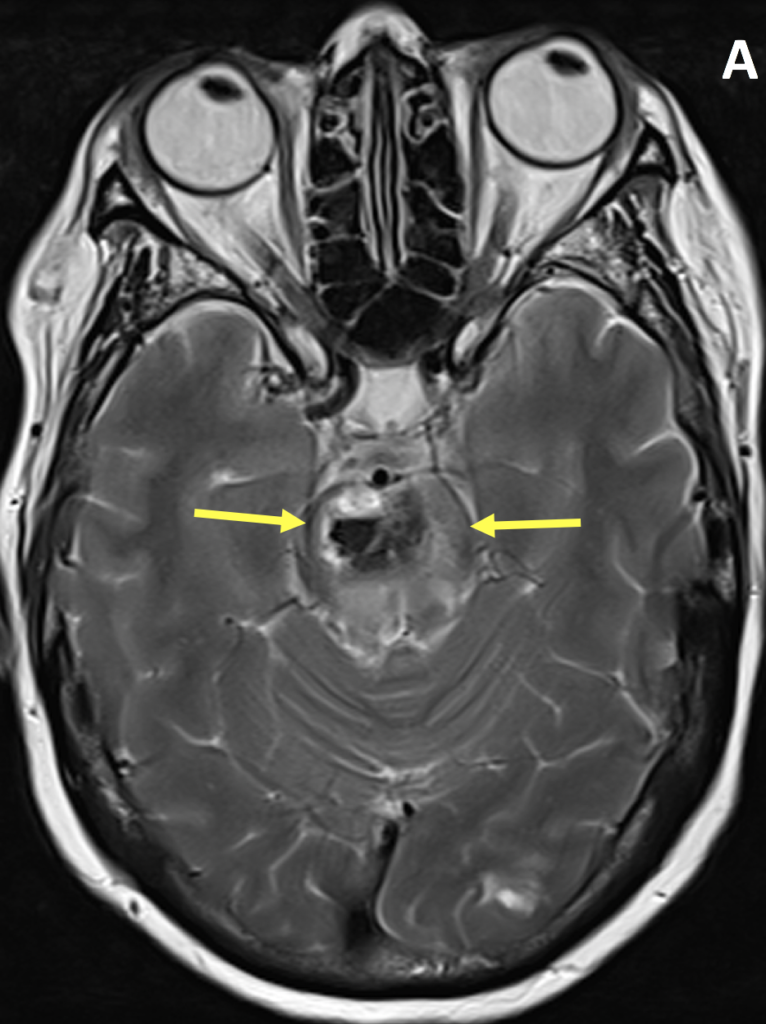
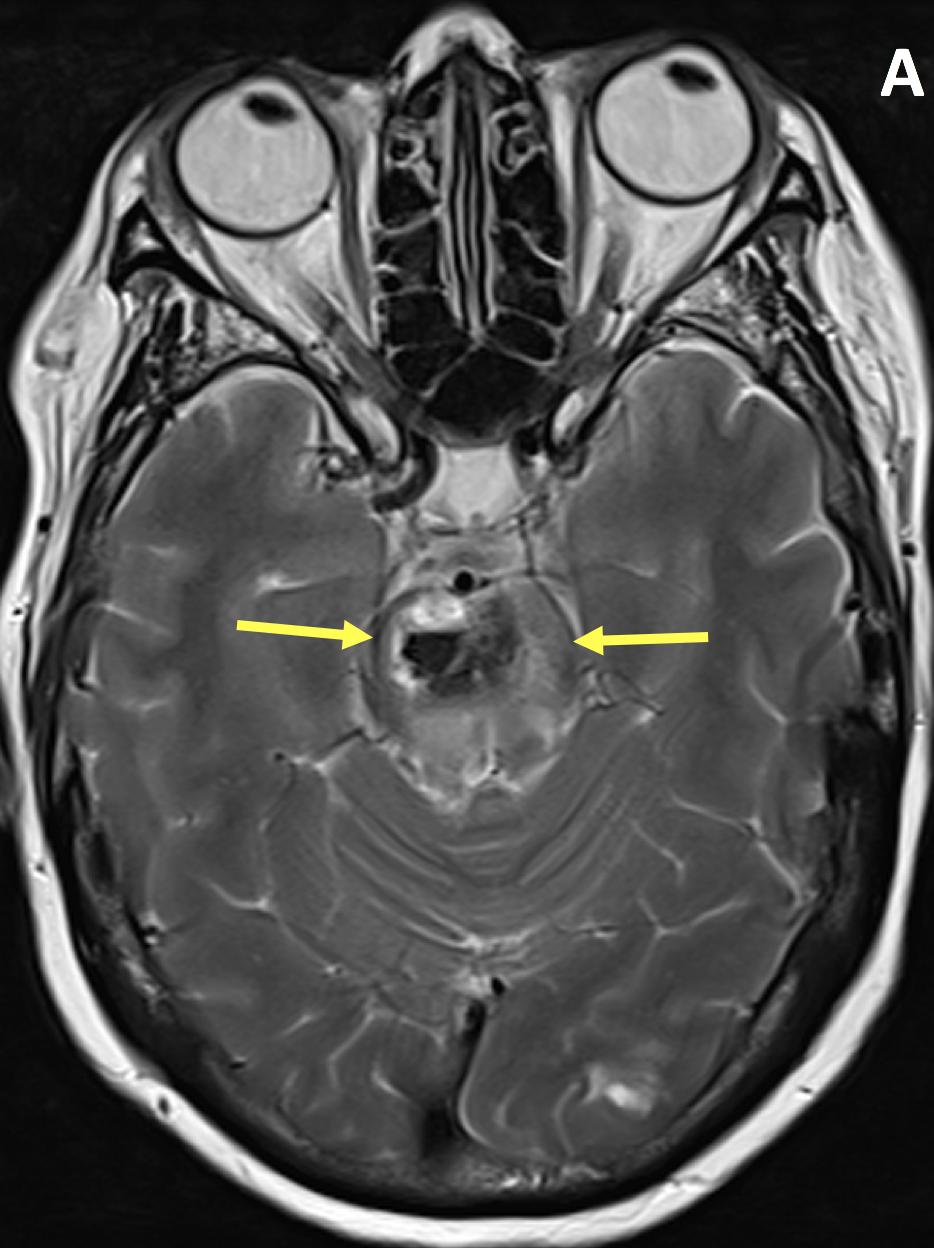
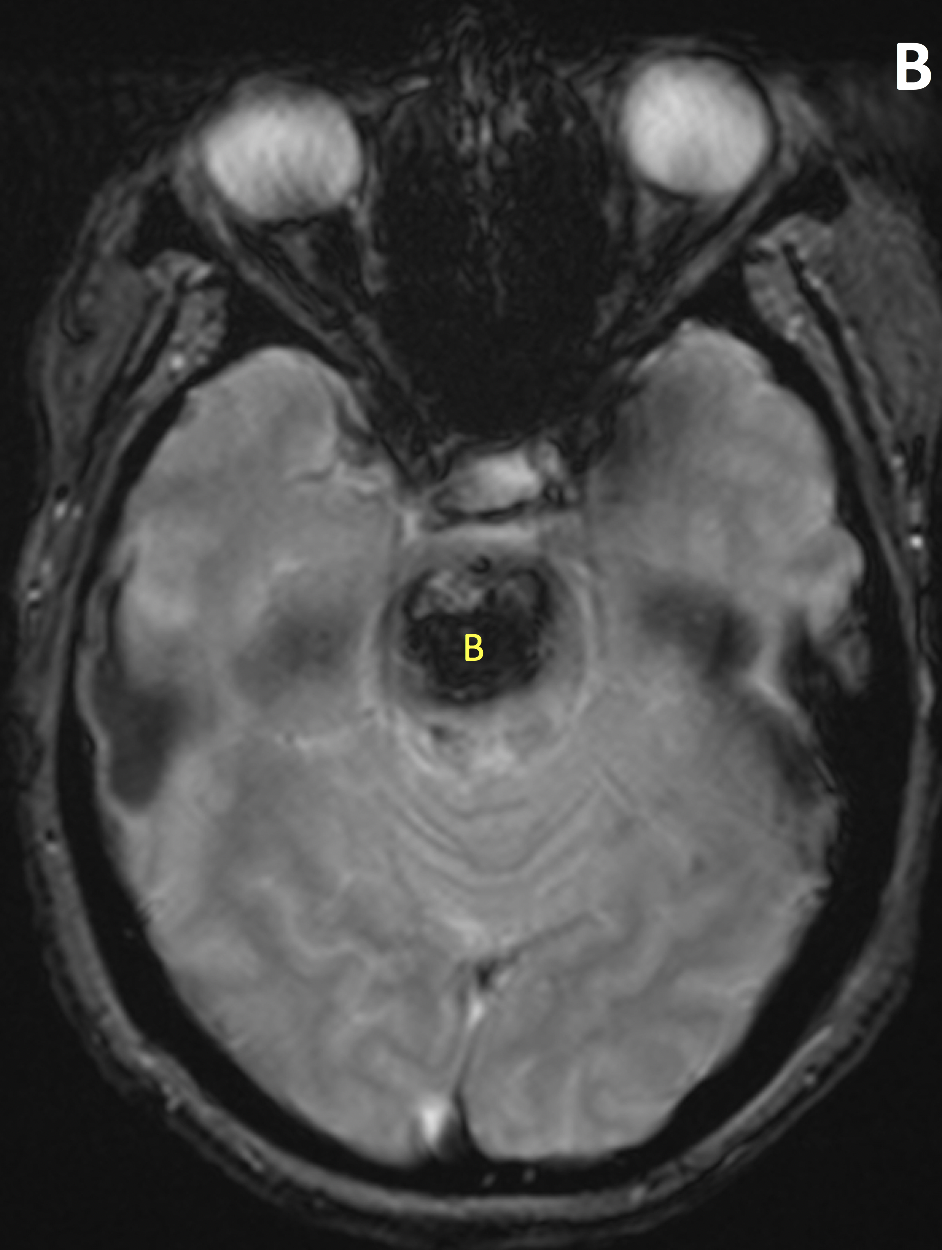
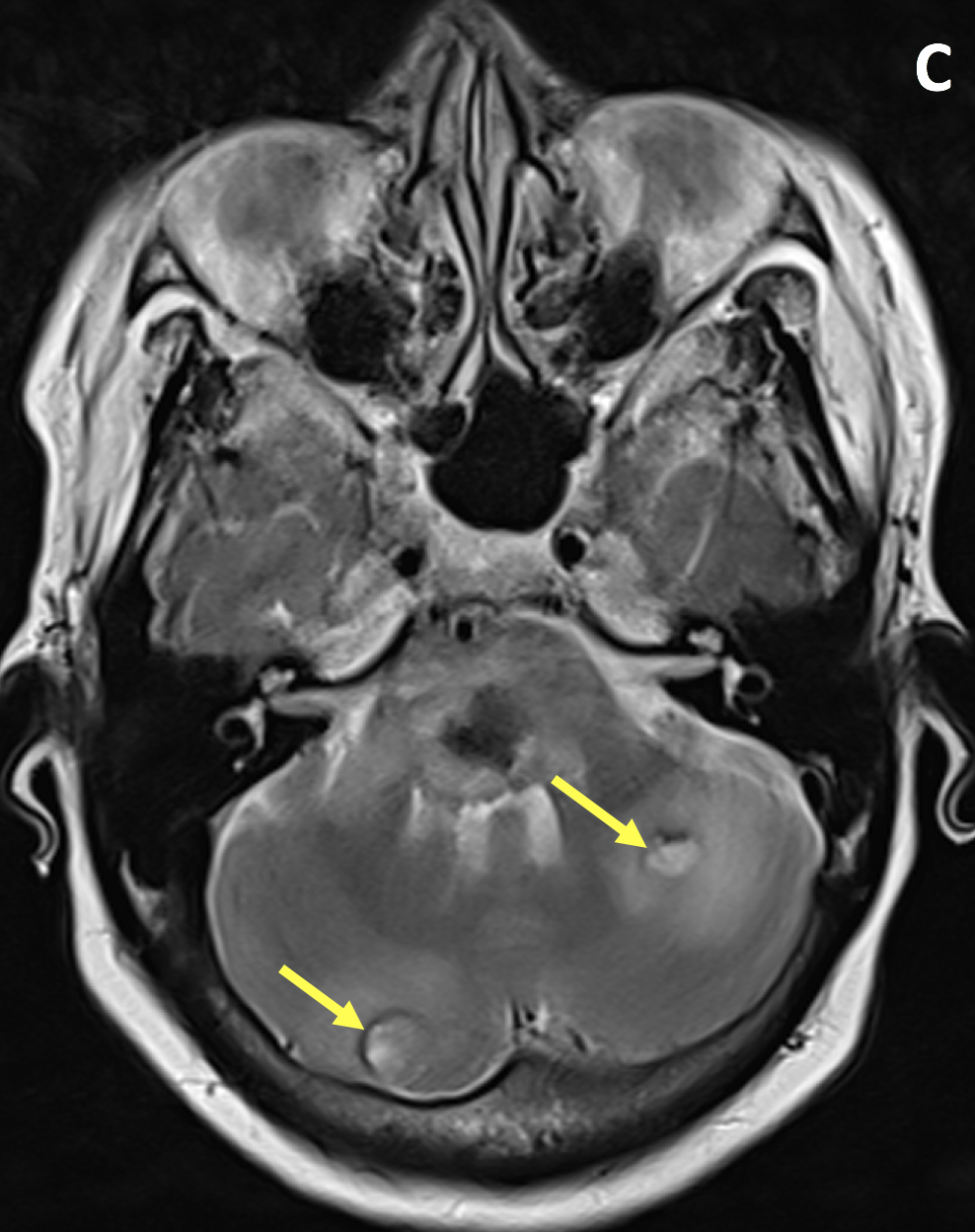
- The MR appearance of ICH is complex and depends primarily on whether the blood is in the deoxyhemoglobin, intracellular methemoglobin, extracellular methemoglobin, or hemosiderin state
- Hypertensive hemorrhage most commonly occurs in the deep gray matter, brainstem and cerebellum, often with intraventricular extension
- Compared with hypertensive ICH, CAA typically spares basal ganglia, uncommonly extends intraventricularly, and is associated with different ages of lobar hemorrhage
- Tumor-associated hemorrhage is heterogeneous in appearance due to mixed signals of hemorrhage, nonhemorrhagic tumor tissue, cystic/necrotic change, and greater degrees of vasogenic edema
Pearls
- MRI gradient echo and susceptibility-weighted imaging is superior to CT in detecting chronic hemorrhages and microbleeds, and better at identifying underlying etiology including structural lesions
- Contrast-enhanced MRI can show rim enhancement of metastatic lesions as well as subacute hematomas
References
- Heit JJ, Iv M, Wintermark M. Imaging of intracranial hemorrhage. J Stroke 2017; 19(1):11-27
- William WG Jr. MRI of intracranial hemorrhage. Contemporary Diagnostic Radiology 2016; 39(10):1-6
Case-based learning.
Perfected.
Learn from world renowned radiologists anytime, anywhere and practice on real, high-yield cases with Medality membership.
- 100+ Mastery Series video courses
- 4,000+ High-yield cases with fully scrollable DICOMs
- 500+ Expert case reviews
- Unlimited CME & CPD hours