Diagnosis Definition
- Intracranial hypotension (IH) is defined as low pressure within the calvarium
- Spontaneous IH is characterized by the classic triad of 1) low cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure, 2) orthostatic headache, and 3) “brain sag”
- IH typically results from a traumatic dural tear and leakage of CSF into the epidural space or is iatrogenic and related to surgery, high volume lumbar puncture, or over-shunting
Imaging Findings
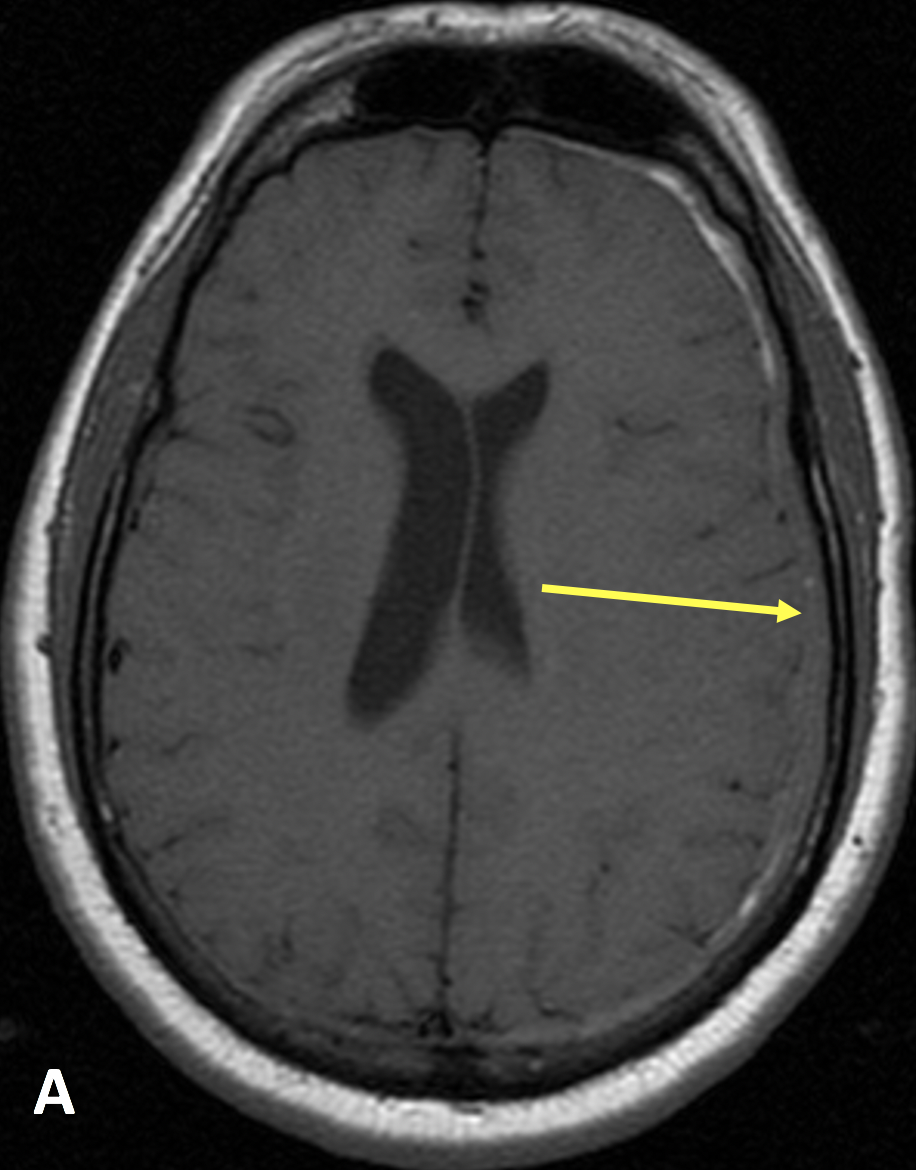
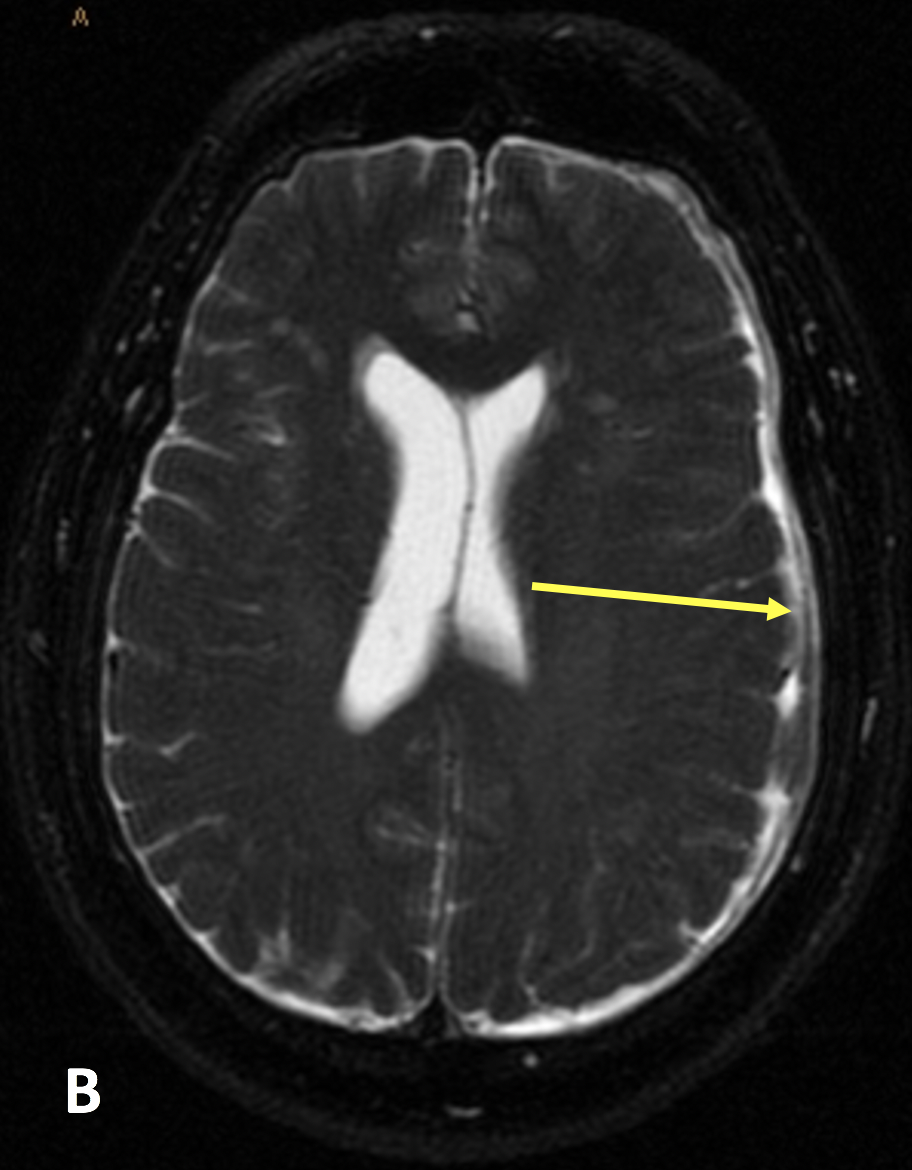
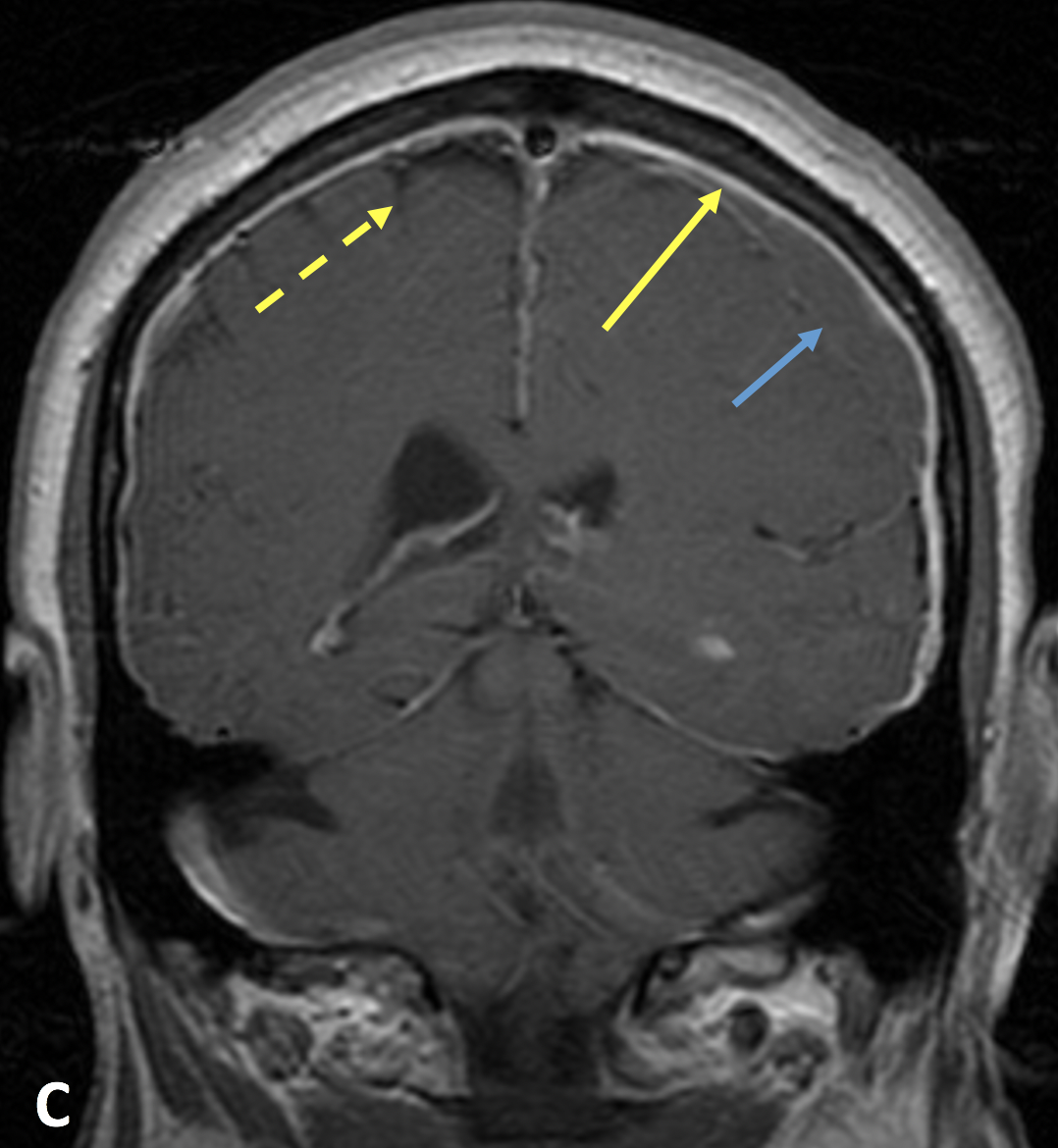
- On post-contrast CT or MRI, IH demonstrates diffuse, smooth pachymeningeal (dural) enhancement that does not involve the sulci (distinct from leptomeningeal enhancement that does involve the sulci)
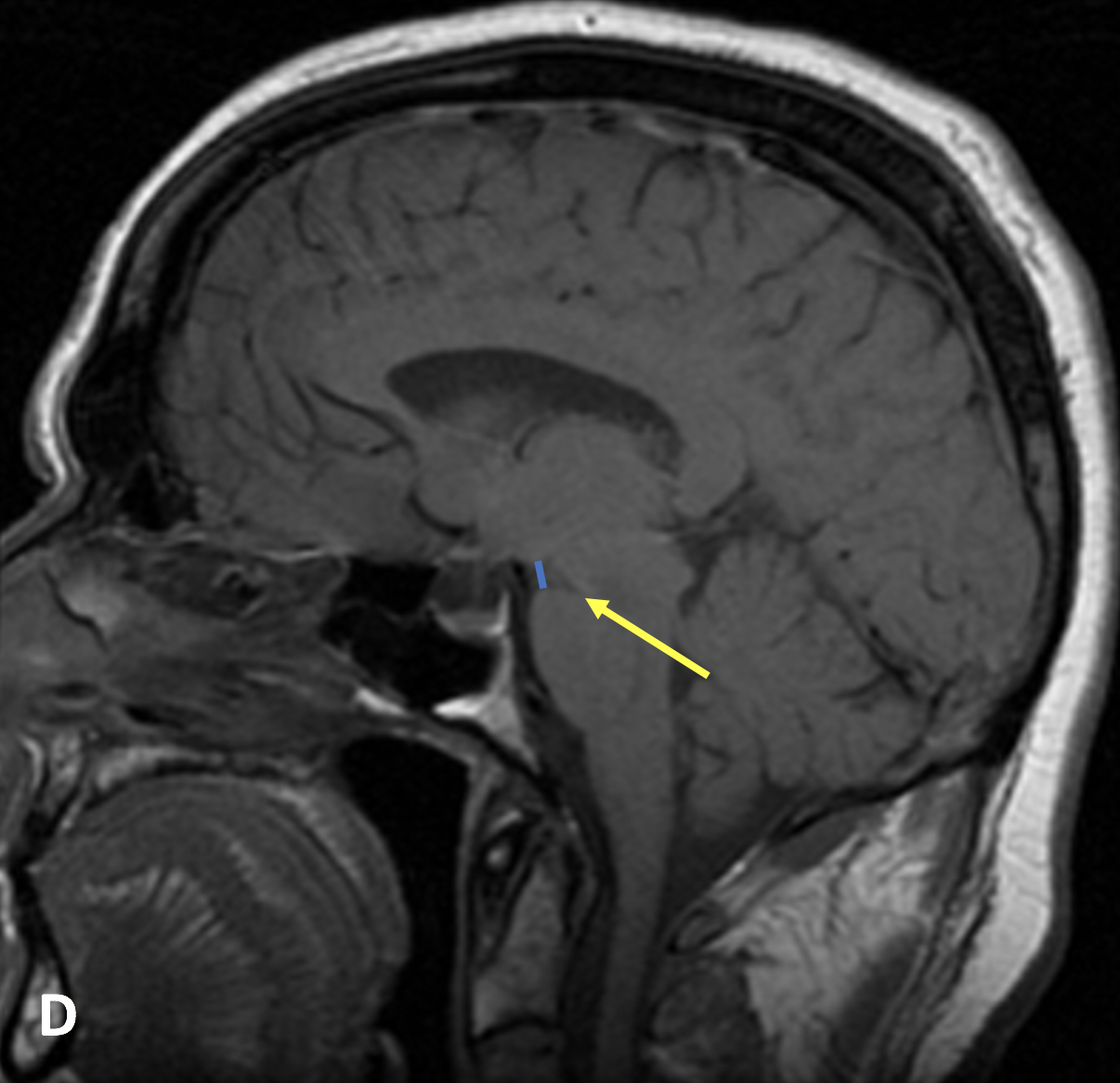
- Midline sagittal MRI sequences show a decreased pontomesencephalic angle (less than 50°, referred to as “midbrain slumping” or “brain sag”) and decreased mamillopontine distance (less than 5.5 mm)
- Obliteration of the prepontine and peri-chiasmatic cisterns, with flattening of the pons and draping of the optic chiasm over the dorsum sella is often seen
- The pituitary and dural sinuses may be enlarged
Pearls
- In IH, the iter (top of the cerebral aqueduct) typically descends below the incisural line, as opposed to Arnold-Chiari malformations where the iter position is usually unchanged
- Differential considerations for pachymeningeal enhancement include metastases (nodular, not smooth), granulomatous processes (smooth or nodular and affecting the basal cisterna), reactive/inflammatory processes (postoperative), and meningiomas
References
- Shah LM, McLean LA, Heilbrun ME, Salzman KL. Intracranial hypotension: improved MRI detection with diagnostic intracranial angles. American Journal of Roentgenology 2013; 200(2):400-407
- Smirniotopoulos JG, Murphy FM, Rushing EJ, Rees JH, Schroeder JW. Patterns of contrast enhancement in the brain and meninges. RadioGraphics 2007; 27(2):525-551
- Schievink WI, Maya MM, Louy C, et al. Diagnostic criteria for spontaneous spinal CSF leaks and intracranial hypotension. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2008; 29(5):853-856
Case-based learning.
Perfected.
Learn from world renowned radiologists anytime, anywhere and practice on real, high-yield cases with Medality membership.
- 100+ Mastery Series video courses
- 4,000+ High-yield cases with fully scrollable DICOMs
- 500+ Expert case reviews
- Unlimited CME & CPD hours