Diagnosis Definition
- Spinal meningiomas are intradural extramedullary lesions, usually benign, that are most commonly thoracic and posterolateral in location
- Accounting for ~25% of spinal tumors, they are the second most common tumor in the intradural extramedullary location, second only to tumors of the nerve sheath (e.g., schwannomas and neurofibromas)
- Most occur in middle-aged or older adults, with female predominance
Imaging Findings
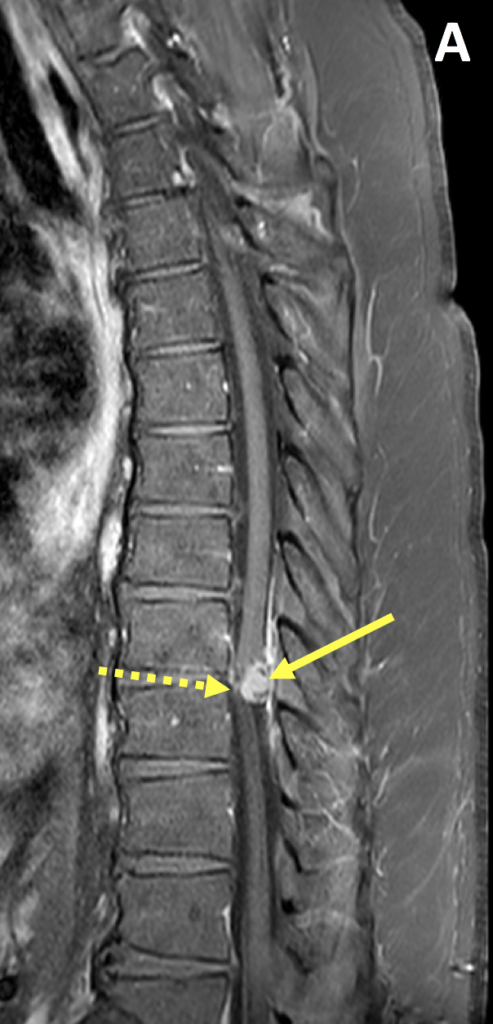
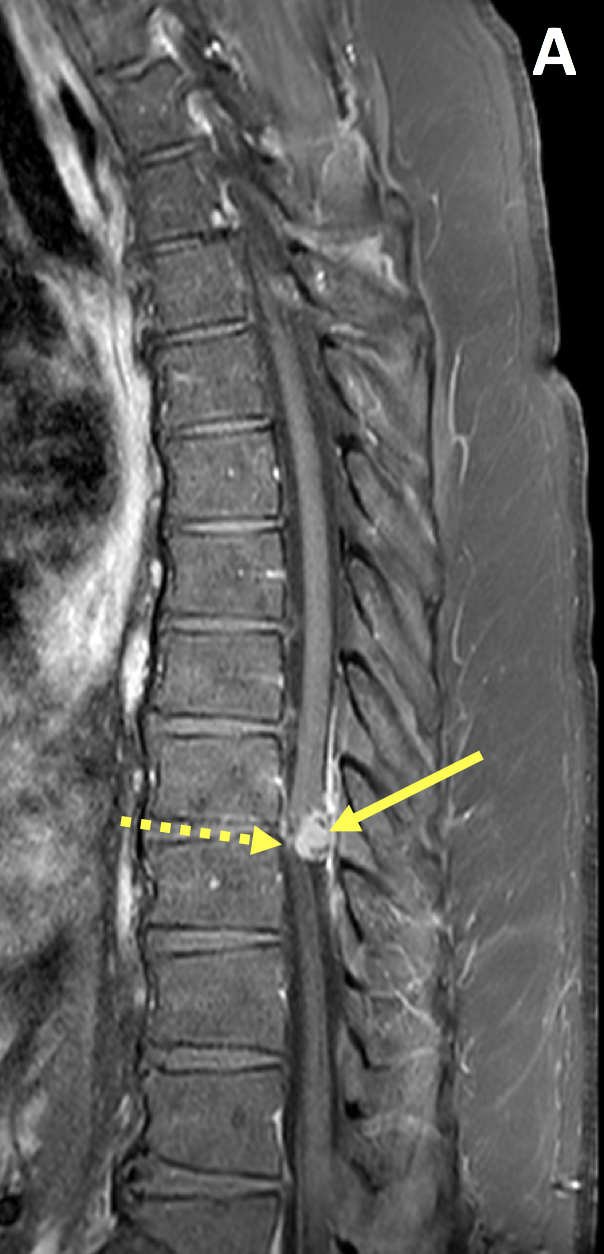
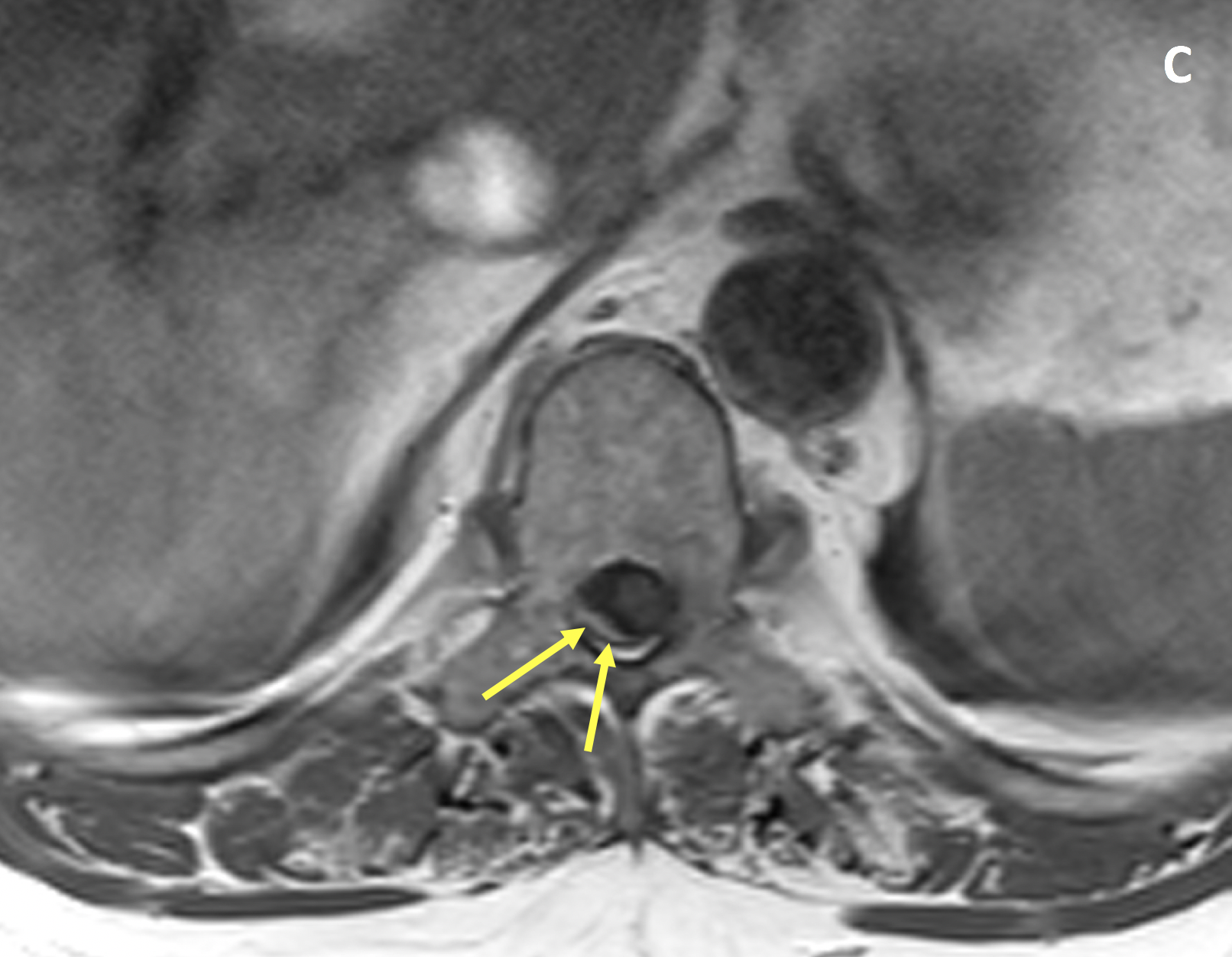
- MRI with contrast is the preferred imaging examination for spinal meningiomas, which are typically isointense to the spinal cord on T1 and T2-weighted images and demonstrate homogeneous avid enhancement
- Other MRI features include displacement/compression of the spinal cord, a meniscus where contrast caps the lesion from above and below, and widened subarachnoid space on the side of the lesion
- Most spinal meningiomas demonstrate broad-based dural attachment with an associated dural tail on postcontrast images
- On occasion, a densely calcified meningioma may demonstrate hypointensity on T1 and T2-weighted images
Pearls
- A meningioma with intradural and extradural components occasionally mimics a nerve sheath tumor and a nerve sheath tumor with a predominant intradural component may mimic a meningioma; however, nerve sheath tumors are usually hyperintense on T2, lumbar and ventral in location, rarely calcified, more common in men, and do not have a dural tail
- CT is better than MRI at showing bony remodeling without bone destruction
- Other intradural extramedullary tumors include lipoma (along the filum terminale and associated with dysraphisms), paraganglioma (occurring in the cauda equina and associated with familial syndrome), ependymoma of the filum, and carcinomatosis (leptomeningeal in location)
References
- Yeo Y, Park C, Lee JW, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging spectrum of spinal meningioma. Clin Imaging 2019; 55:100-106
- De Verdelhan O, Haegelen C, Carsin-Nicol B, et al. MR imaging features of spinal schwannomas and meningiomas. J Neuroradiol 2005; 32(1):42-49
Case-based learning.
Perfected.
Learn from world renowned radiologists anytime, anywhere and practice on real, high-yield cases with Medality membership.
- 100+ Mastery Series video courses
- 4,000+ High-yield cases with fully scrollable DICOMs
- 500+ Expert case reviews
- Unlimited CME & CPD hours