Diagnosis Definition
- Optic glioma is the most common primary neoplasm of the optic nerve
- The optic chiasm, optic tracts, and optic radiations can be involved
- The tumors are usually benign in children and aggressive in adults; 90% present before age 20
- Adults can get optic nerve glioblastomas, whereas optic gliomas are a disease of childhood and neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)
- Optic gliomas are usually unilateral except in patients with NF1; up to 20% of patients with NF1 have optic gliomas
Imaging Findings
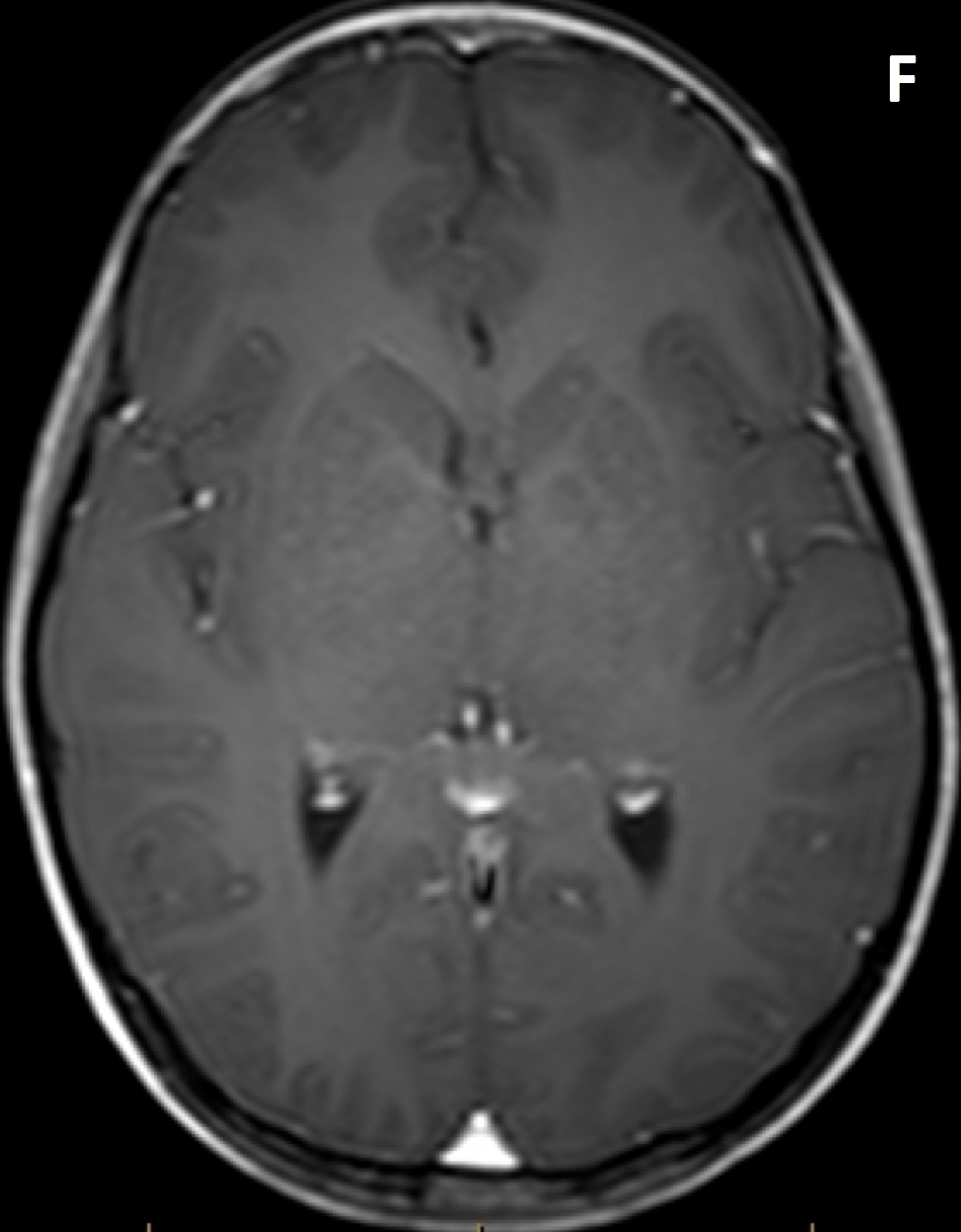
- MRI is better than CT for evaluating the optic nerve, optic chiasm, and optic radiations
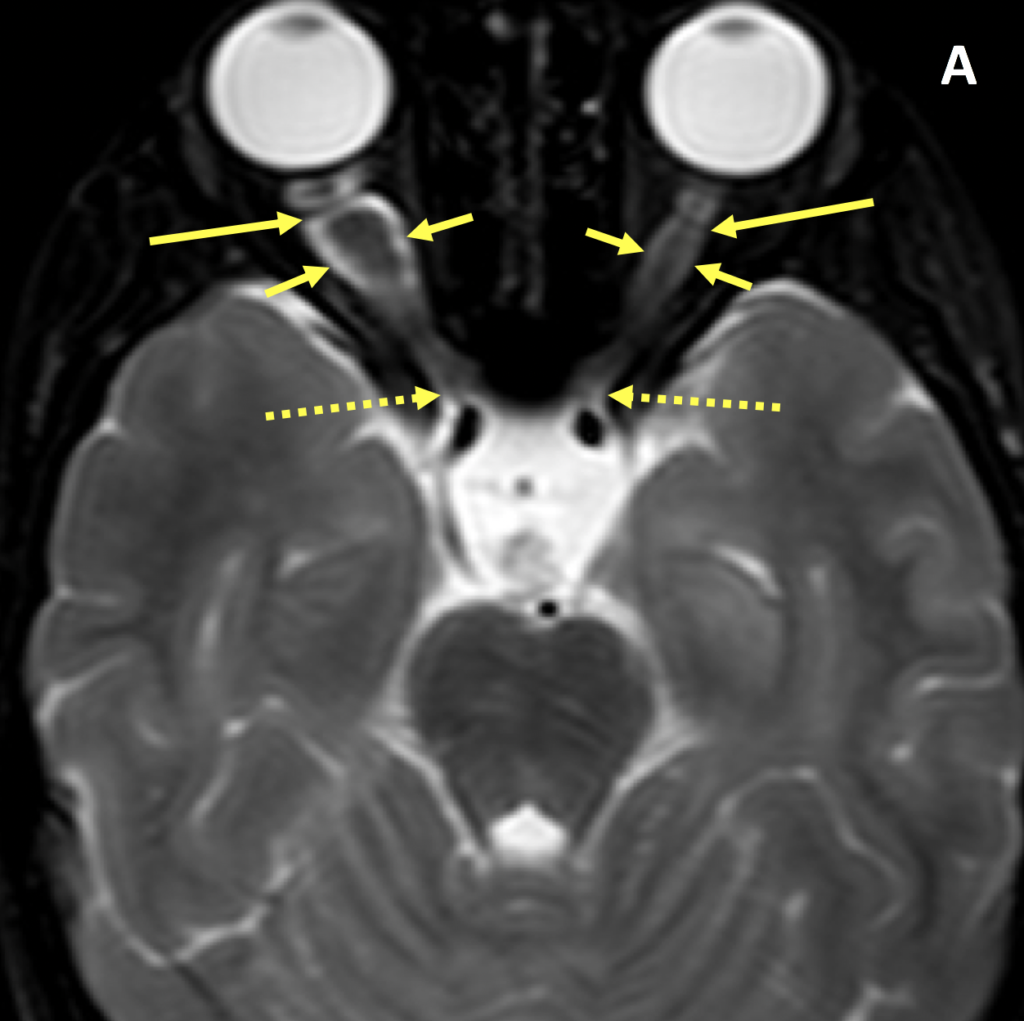
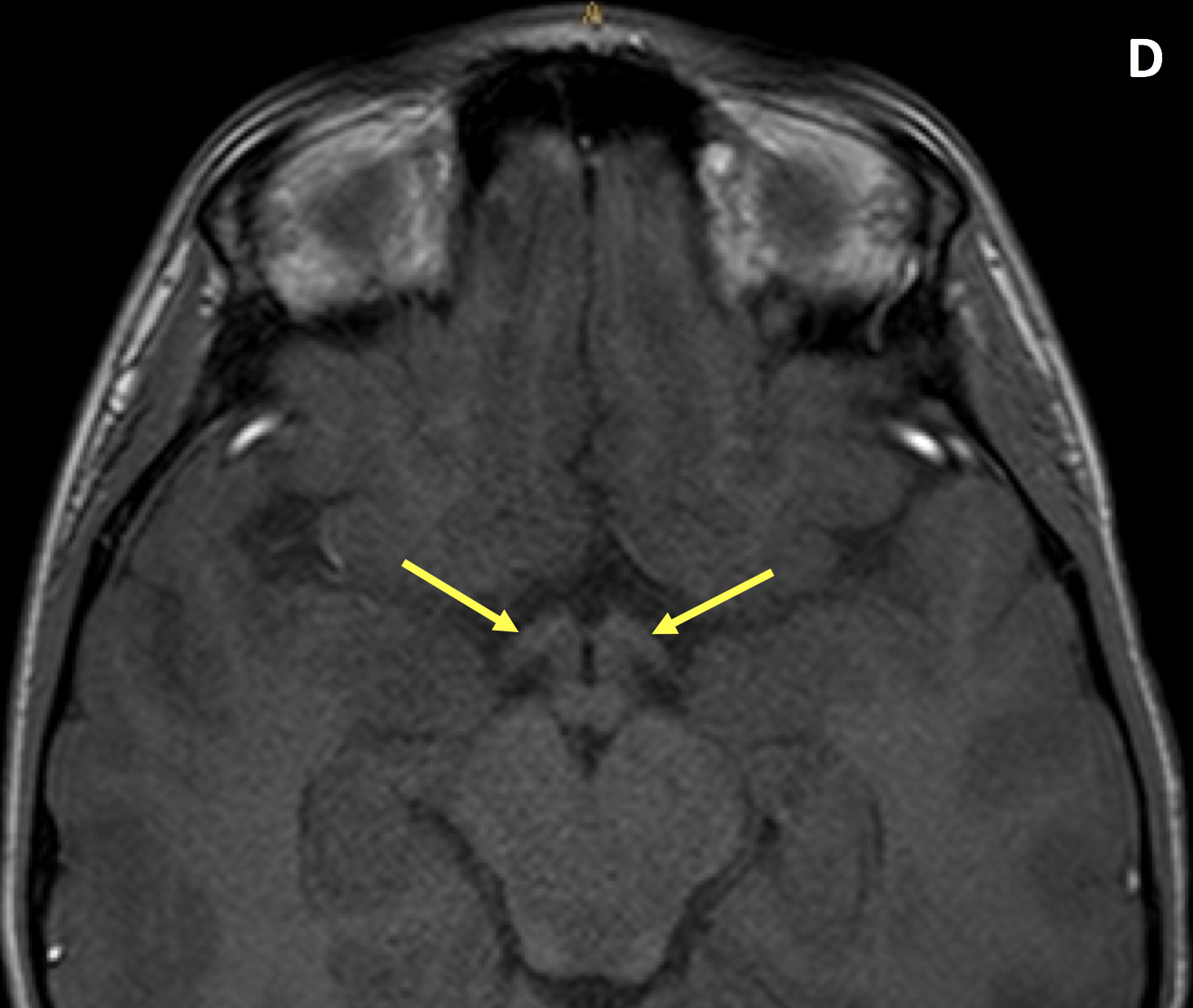
- MRI shows tubular or fusiform enlargement of the optic nerve, with kinking or buckling
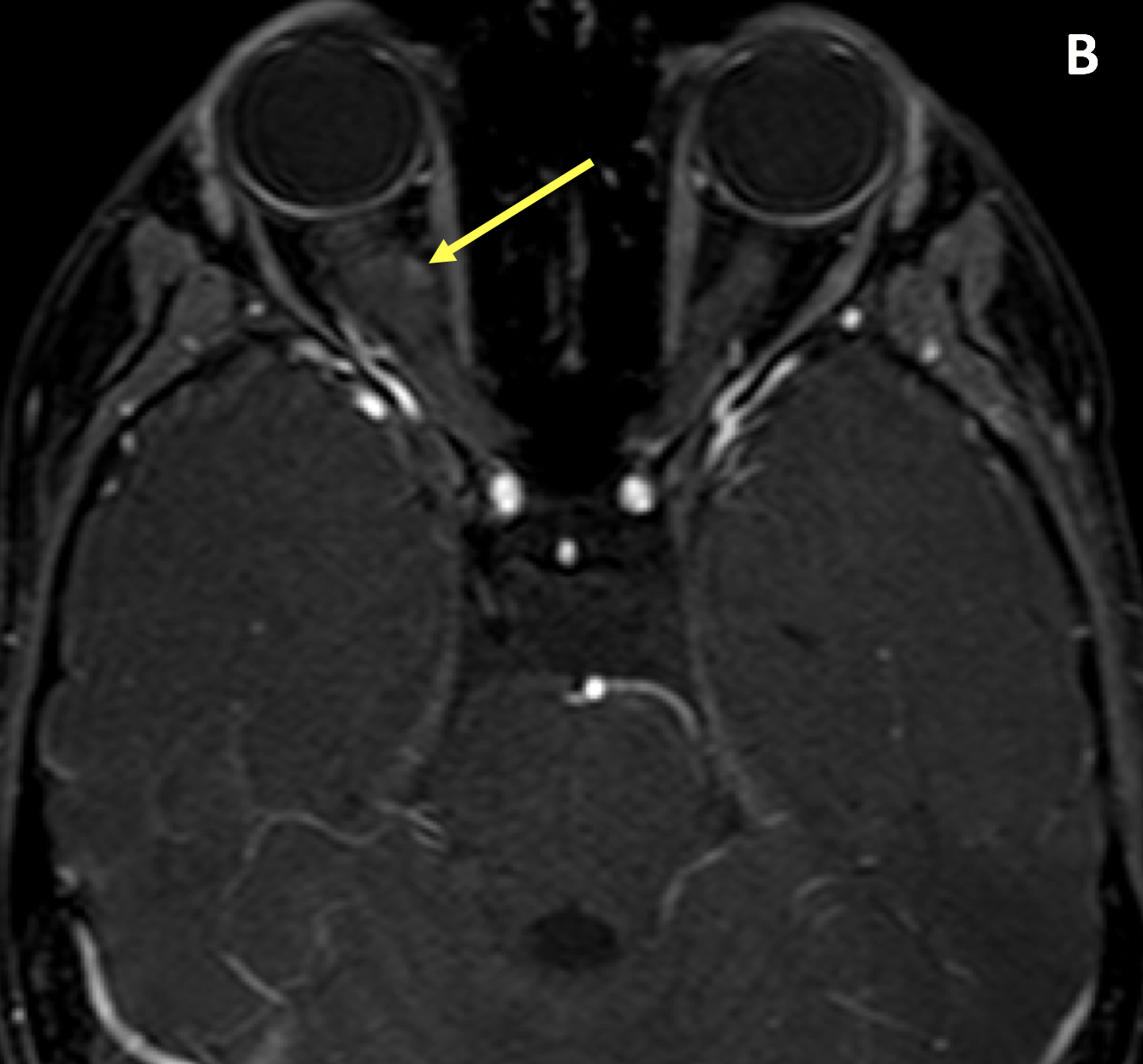
- Optic gliomas are typically isointense to cortex and hypointense to white matter and orbital fat on T1; they are isointense to hyperintense relative to white matter and the cortex on T2; intense enhancement is common, although optic nerve glioblastomas in adults may only minimally enhance as they are low grade astrocytomas
- The bony optic canal may be widened if the intracanalicular segment of the nerve is involved
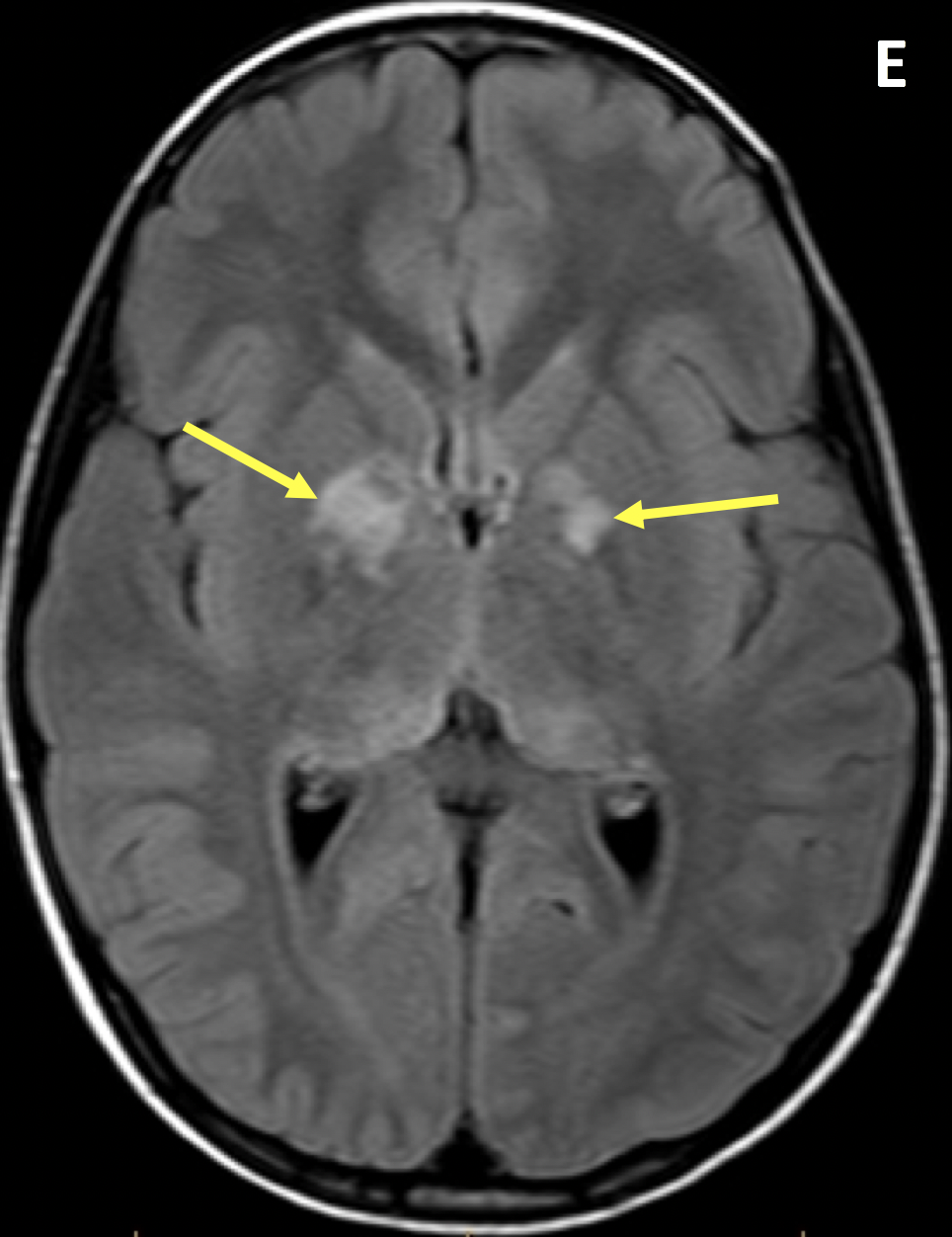
- If associated with NF1, hyperintense lesions can be seen in the cerebellum, brain stem, basal ganglia, thalamus, periventricular white matter, and corpus callosum without mass effect, edema, or enhancement
Pearls
- Optic glioma can be diagnosed with a high degree of confidence when it involves the optic chiasm and retrochiasmatic optic pathway
- Although MRI is the ideal imaging modality to evaluate the optic nerve, CT is better at showing erosion or expansion of the optic canal
- Meningioma, the primary differential diagnostic consideration, is characterized by peripheral enhancement of the optic nerve sheath (aka, “tram-track” sign), whereas enhancement of optic gliomas is more uniform
- Calcification, seen in meningiomas but not gliomas, is best seen on CT
References
- Smith MM, Strottmann JM. Imaging of the optic nerve and visual pathways. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 2001; 22(6):473-487
Case-based learning.
Perfected.
Learn from world renowned radiologists anytime, anywhere and practice on real, high-yield cases with Medality membership.
- 100+ Mastery Series video courses
- 4,000+ High-yield cases with fully scrollable DICOMs
- 500+ Expert case reviews
- Unlimited CME & CPD hours