Diagnosis Definition
- A ranula is a mucous retention cyst (aka, mucocele) in the floor of the mouth that typically results from trauma or inflammation of the minor salivary or sublingual glands
- Glandular inflammation may be a result of ductal obstruction by a sialolith, inspissated secretions, trauma, or neoplasm
- 70% present in adolescents less than 20 years old but they also occur in the third decade
- Because they have an epithelial layer they can recur if not completely resected
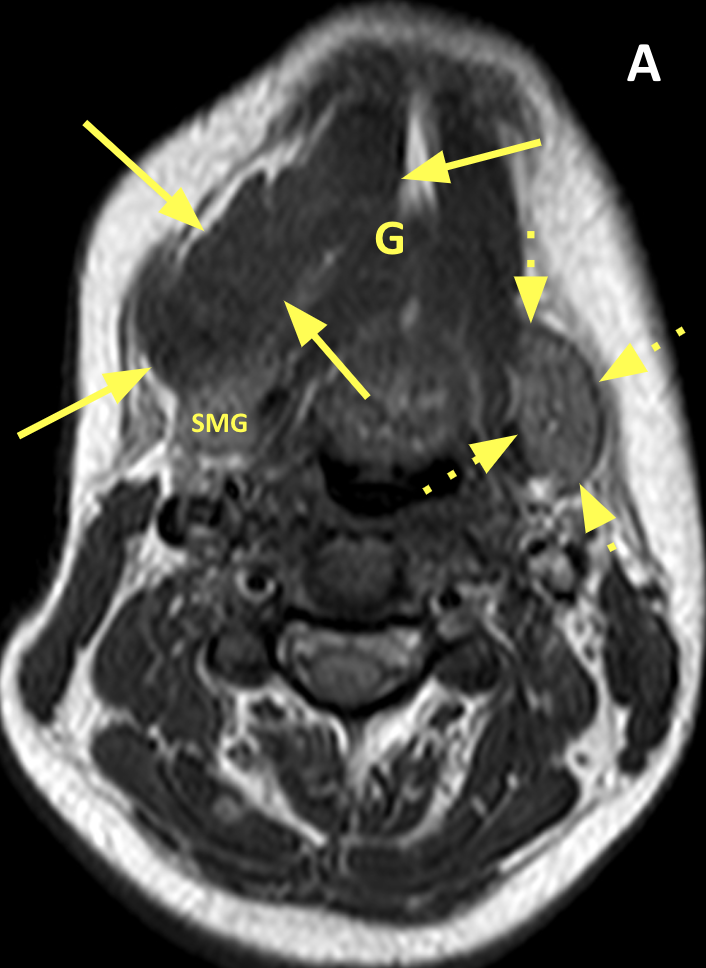
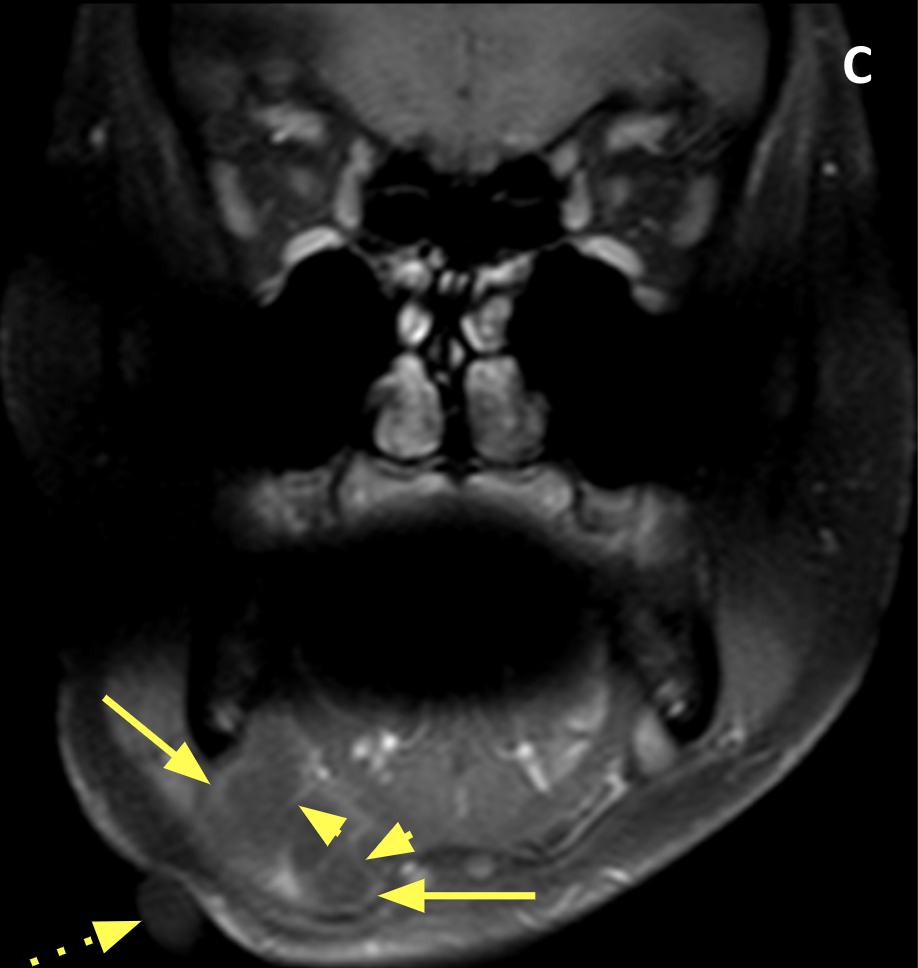
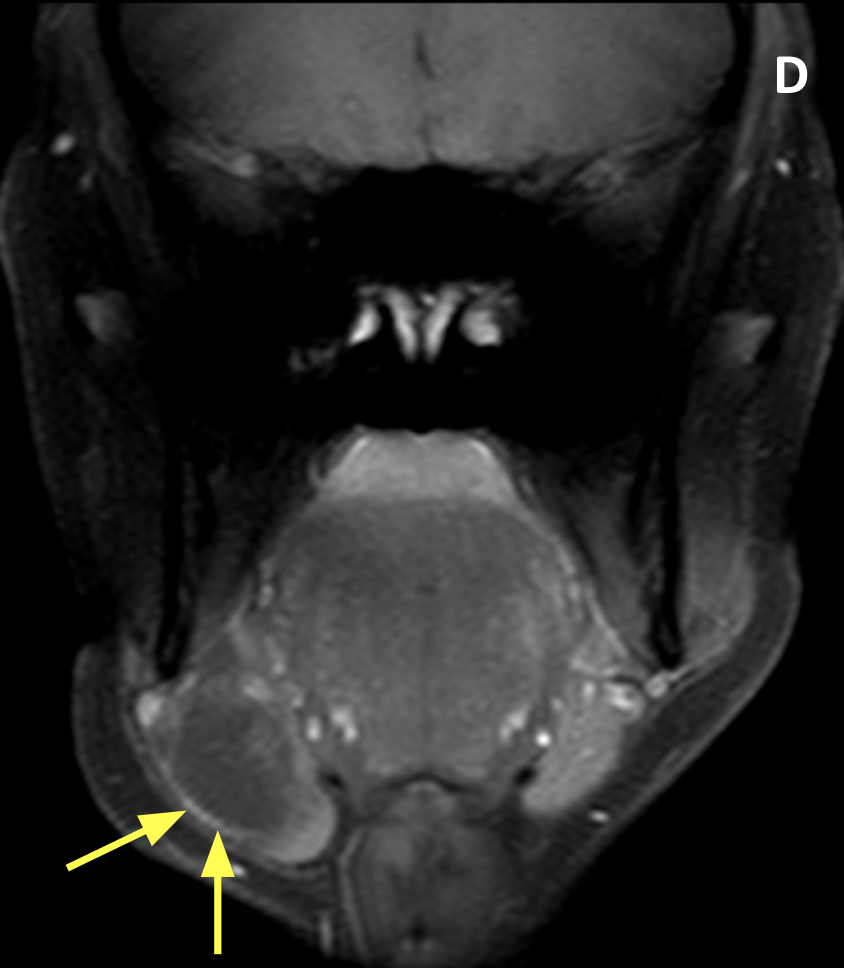
- Ranulas can be simple (confined to the sublingual space) or plunging/diving (extending posteriorly or through a rent in the mylohyoid muscle into the submandibular space and/or parapharyngeal space
Imaging Findings
- MRI typically shows a unilocular, homogeneous, well-defined, nonenhancing cystic mass with low signal on T1 and high signal on T2-weighted images; high signal on T1 indicates a high protein content
- Communication between the sublingual and submandibular components typically occurs behind the posterior free edge of the mylohyoid muscle, creating a smooth tapered continuation anteriorly into the sublingual space (the so-called “tail” sign) or laterally via a congenital defect in the mylohyoid muscle
- Recurrent and previously infected ranulas may show atypical features, such as septation and rim enhancement
Pearls
- A defect in the mylohyoid muscle (aka, “boutonniere”) is a normal anatomic variant seen on 77% of CT examinations
- A lesion that shows other findings such as involvement of other anatomic spaces, lack of a smooth tapered tail extending into the sublingual space, lobulation, septation, heterogeneity, enhancement, or fluid-fluid levels in a younger patient should raise the possibility of a cystic hygroma
References
- Macdonald AJ, Salzman KL, Harnsberger HR. Giant ranula of the neck: differentiation from cystic hygroma. American Journal of Neuroradiology 2003; 24(4):757-761
- Kurabayashi T, Ida M, Yasumoto M, et al. MRI of ranulas. Neuroradiology 2000; 42:917–922
Case-based learning.
Perfected.
Learn from world renowned radiologists anytime, anywhere and practice on real, high-yield cases with Medality membership.
- 100+ Mastery Series video courses
- 4,000+ High-yield cases with fully scrollable DICOMs
- 500+ Expert case reviews
- Unlimited CME & CPD hours