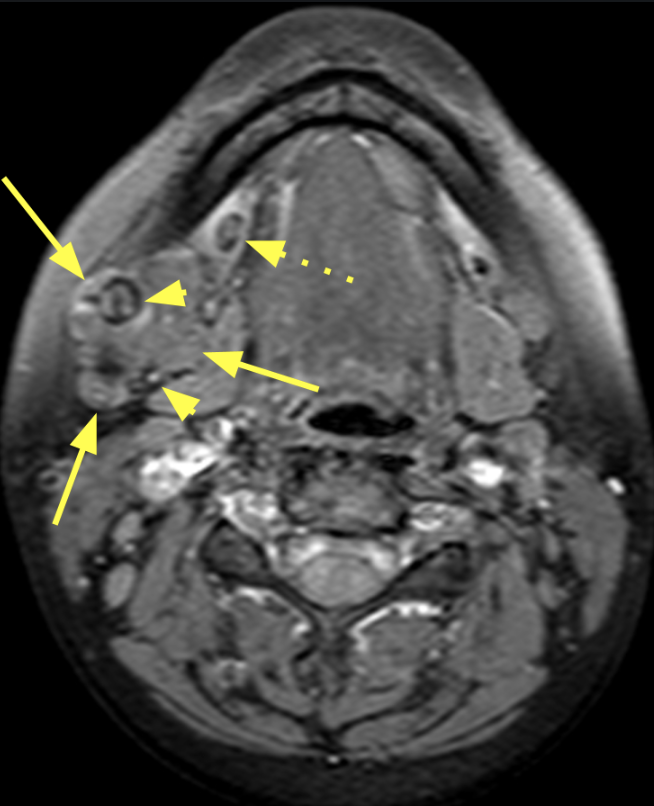
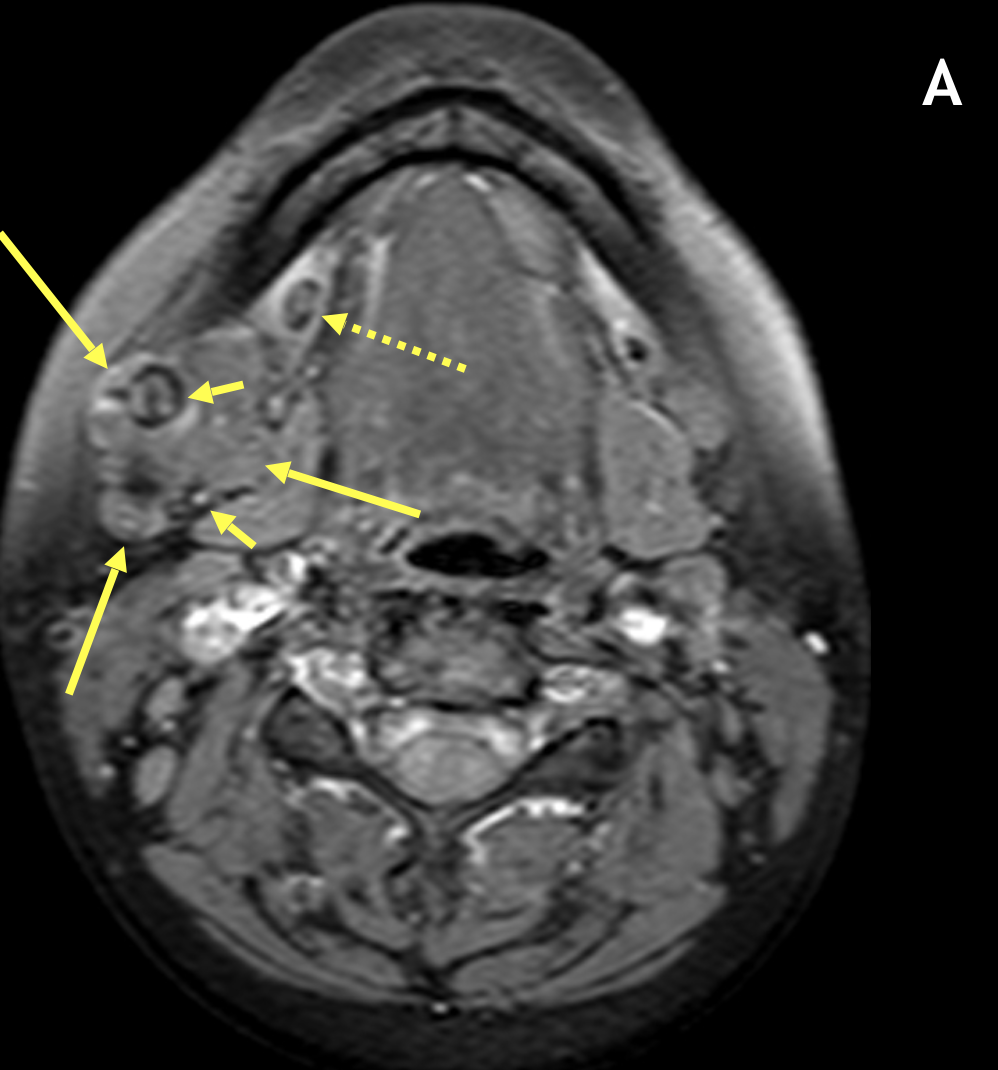
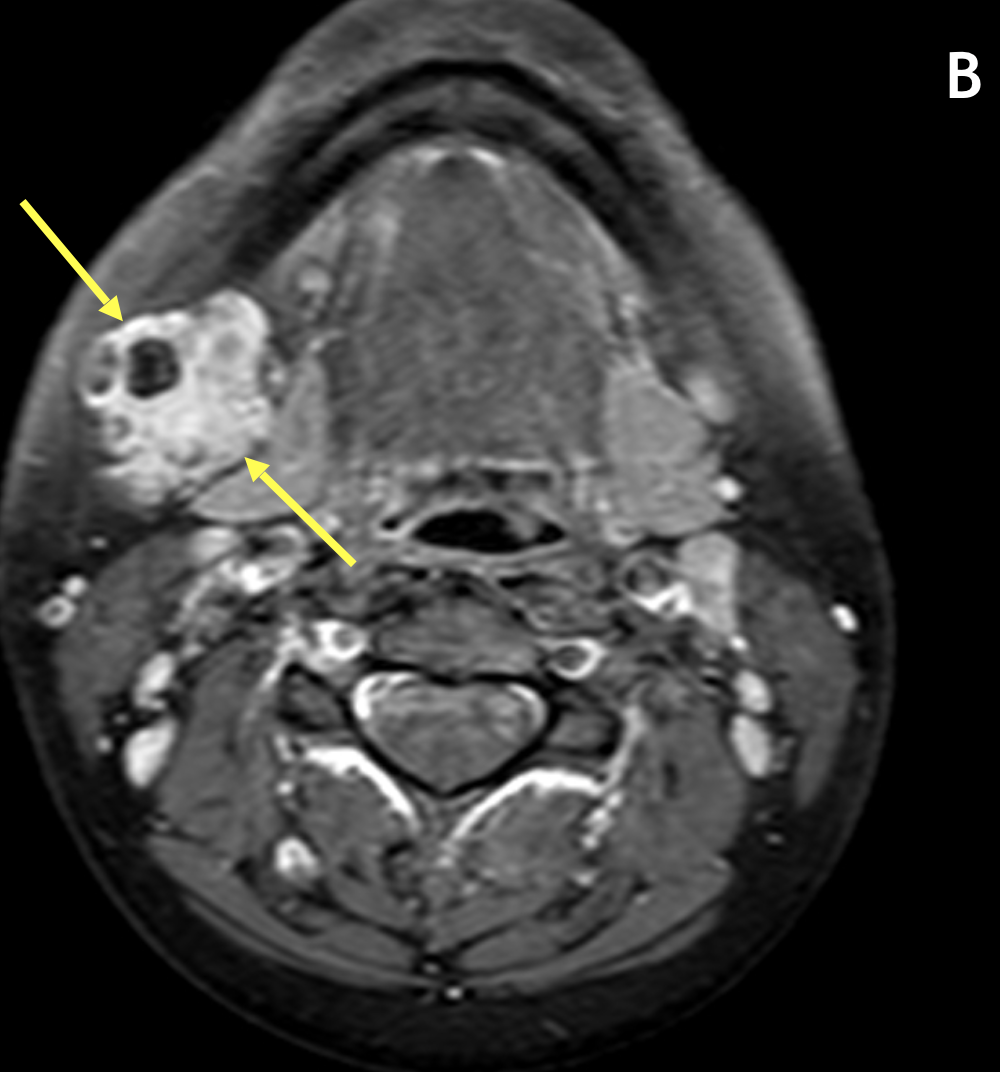
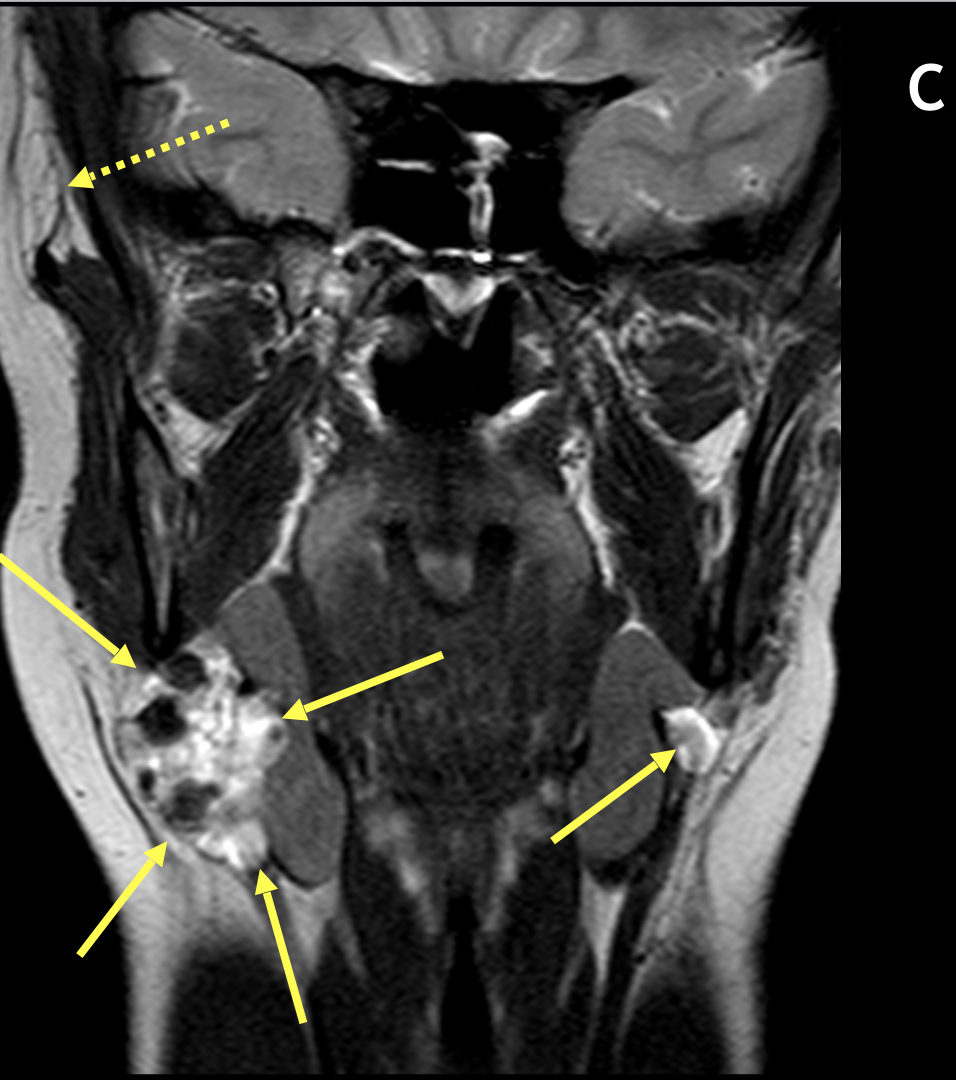
Diagnosis Definition
- Sialolithiasis (salivary gland calculi) is the most common benign condition affecting the salivary glands and the most common cause of sialadenitis (inflammation of the salivary glands)
- The submandibular (Wharton) duct is involved in 80-90% of cases, followed by the parotid (Stensen) duct in 10-20%
- The submandibular gland is most often involved because of the nature of its duct system (relatively large, sharply angled, and ascending) and secretions (mucinous, alkaline, and viscous)
- Most calculi are radiopaque
Imaging Findings
- Axial and coronal T1 and T2-weighted sequences are generally obtained
- Contrast can help distinguish solid from cystic components and evaluate the margins of the gland
- The involved gland, often diffusely or focally enlarged, can range from well-defined to poorly defined; there may be associated fascial thickening and infiltration of subcutaneous fat (i.e., “dirty fat”)
- Signal characteristics vary with chronicity; heterogeneous low signal on T1 and high signal on T2 are seen in acute cases with low-to-intermediate signal on T2 in chronic cases
- MR sialography is a noninvasive method to characterize the ductal structures and is as accurate as conventional sialography in detecting obstructions, stenosis and stricture
Pearls
- The main differential diagnoses are Sjφgren syndrome and sarcoidosis
- Sialolithiasis is the most common cause of unilateral enlargement of the salivary glands
- Viral parotiditis is usually bilateral and may also involve the submandibular gland
- An important advantage of MR sialography is the fact that the structural anatomy of the salivary glands remains unchanged, whereas with ultrasound, the parenchyma and ducts may be compressed by the transducer
References
- Yousem DM, Kraut MA, Chalian AA. Major salivary gland imaging. Radiology 2000; 216:19–29
- Shah GV. MR imaging of salivary glands. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 2004; 14:777–808
Case-based learning.
Perfected.
Learn from world renowned radiologists anytime, anywhere and practice on real, high-yield cases with Medality membership.
- 100+ Mastery Series video courses
- 4,000+ High-yield cases with fully scrollable DICOMs
- 500+ Expert case reviews
- Unlimited CME & CPD hours