Diagnosis Definition
- >90% of oral cavity (including anterior tongue and floor of mouth), pharynx (nasopharynx, oropharynx, including posterior tongue, and hypopharynx), and laryngeal malignancies are squamous cell carcinoma (SCCa); tumors are staged by the TNM (tumor, nodes, metastases) classification
- Risk factors for SCCa include long-term overuse of alcohol and tobacco and human papillomavirus (HPV)
- Approximately 65% of patients with oropharyngeal SCCa present with metastatic cervical lymphadenopathy; the most frequent sites of SCCa causing regional metastases are base of the tongue and tonsil
- SCCa in the base of the tongue often manifests with dysphagia, odynophagia, or the sensation of a mass
Imaging Findings
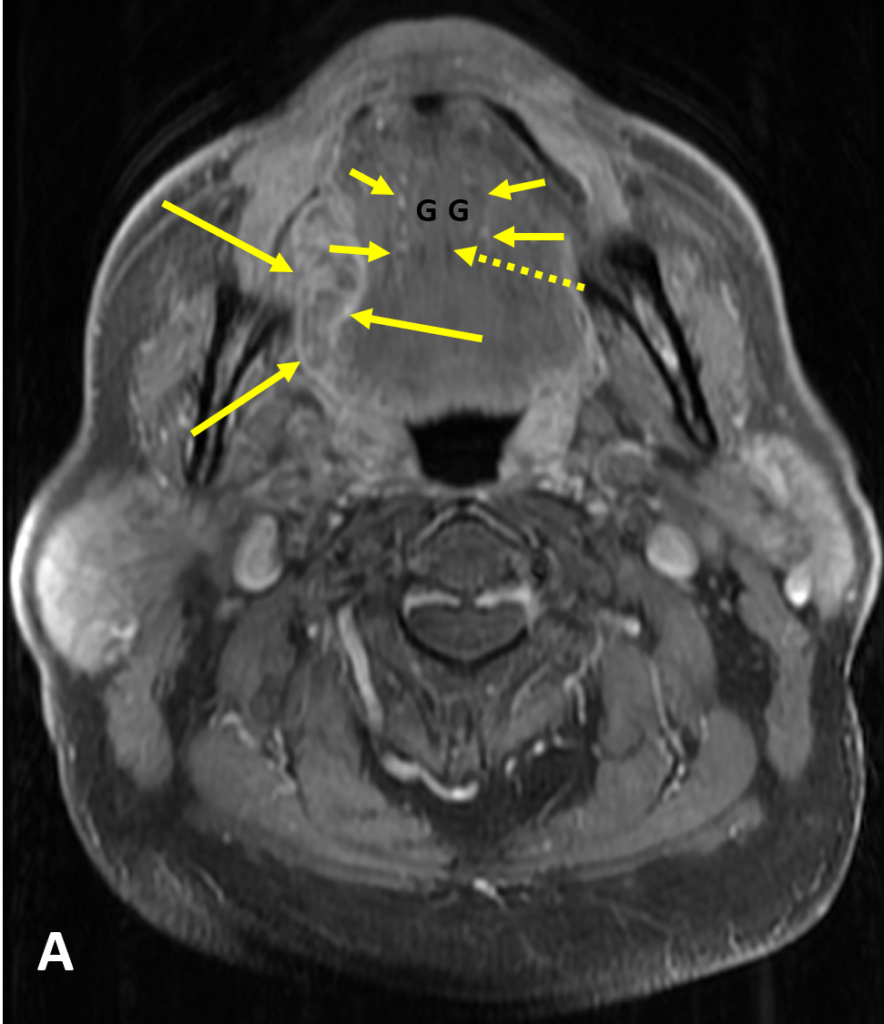
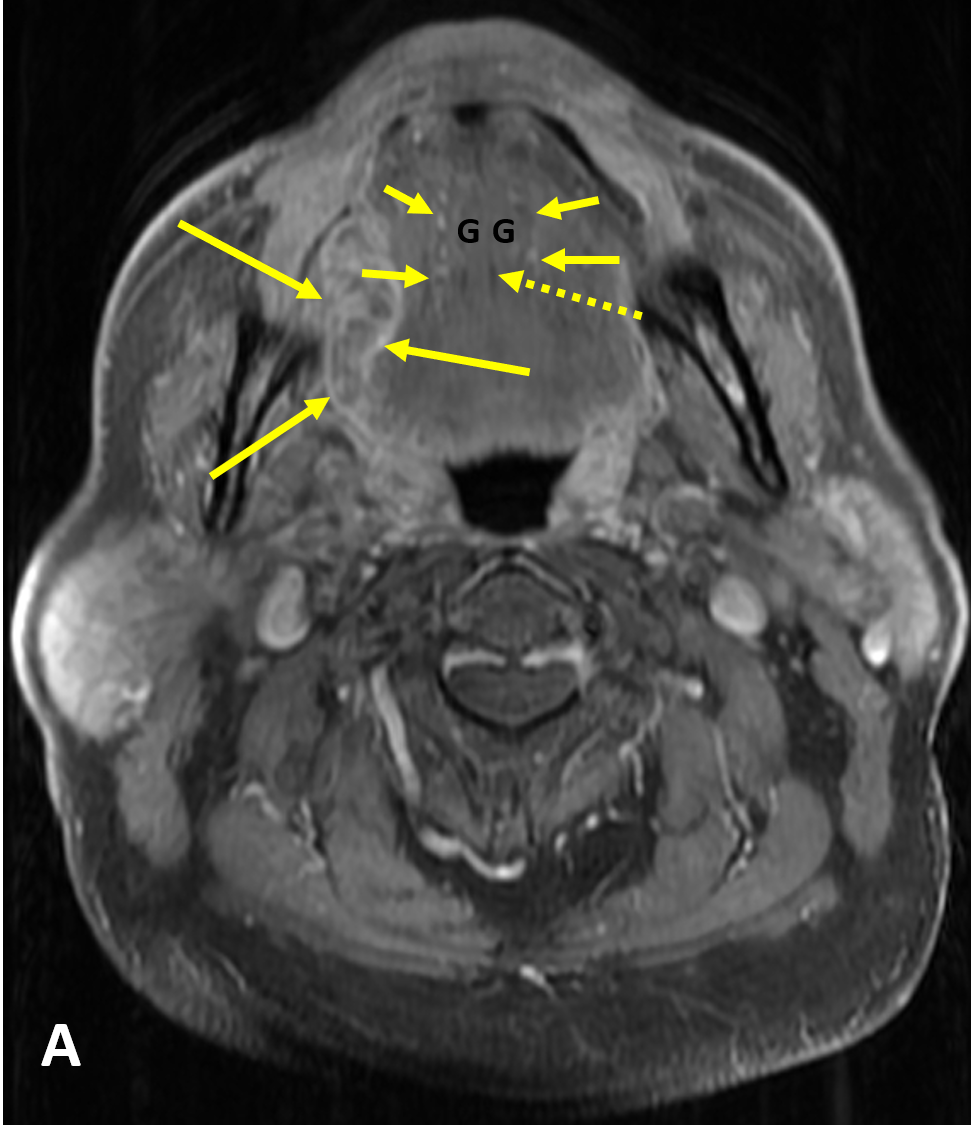
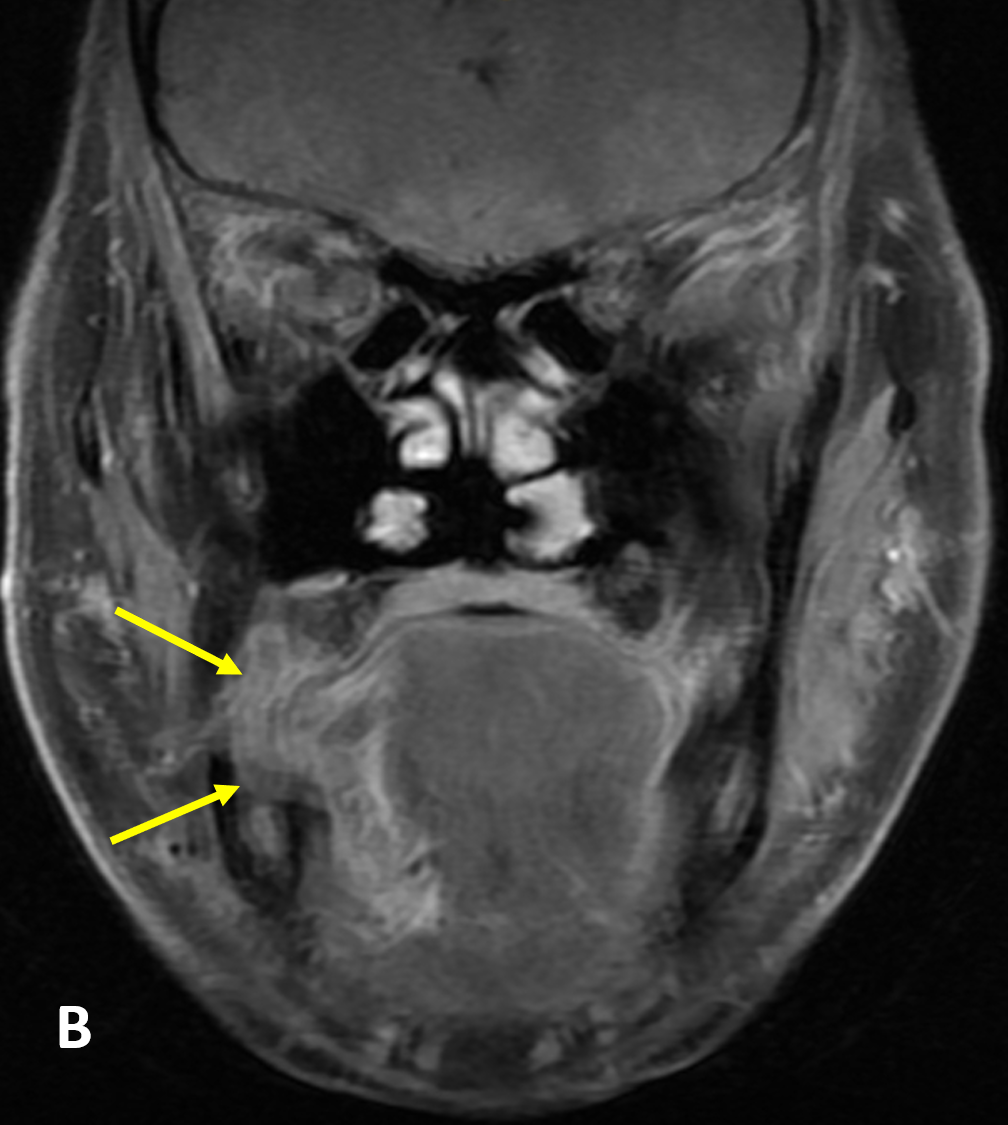
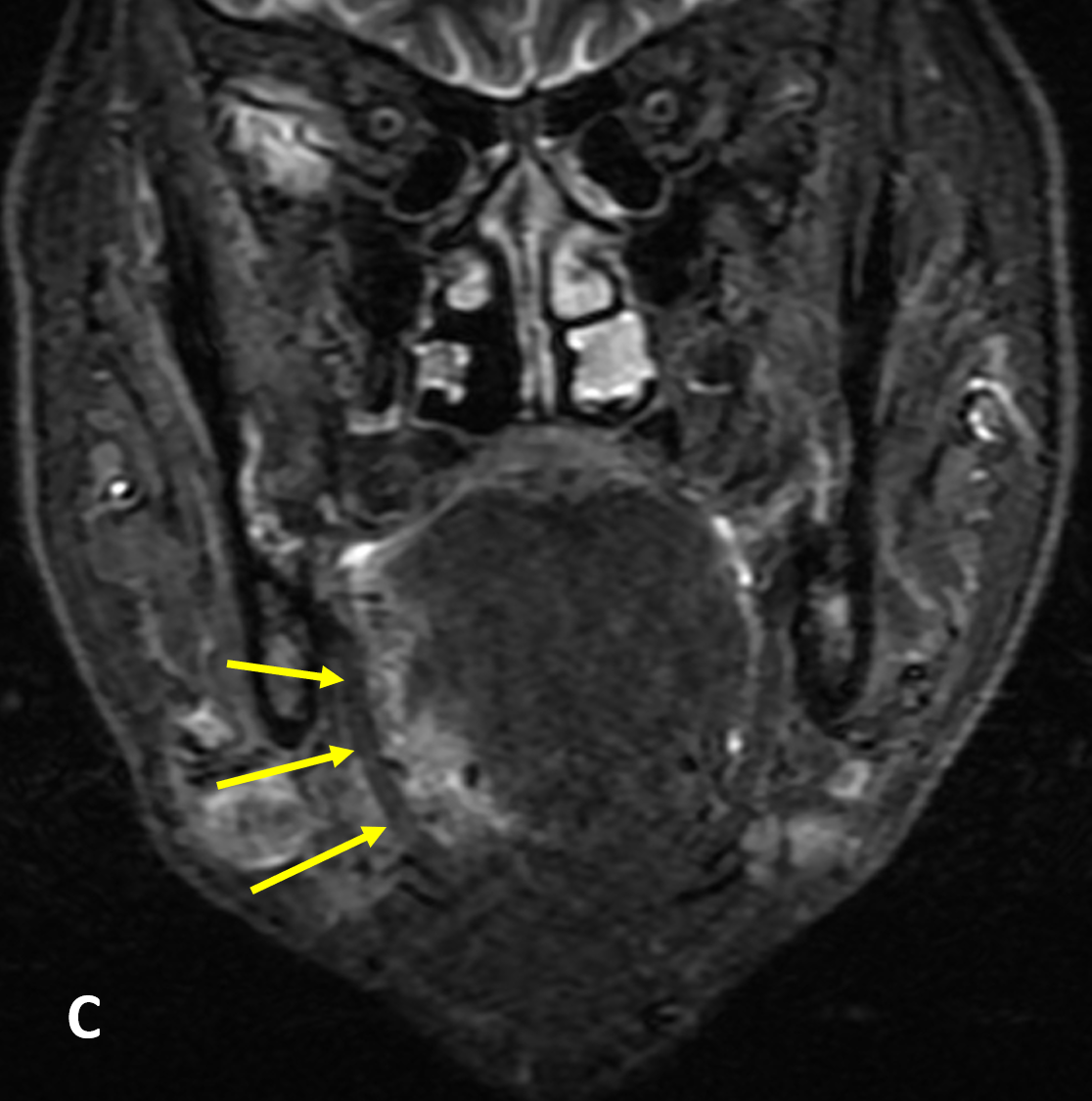
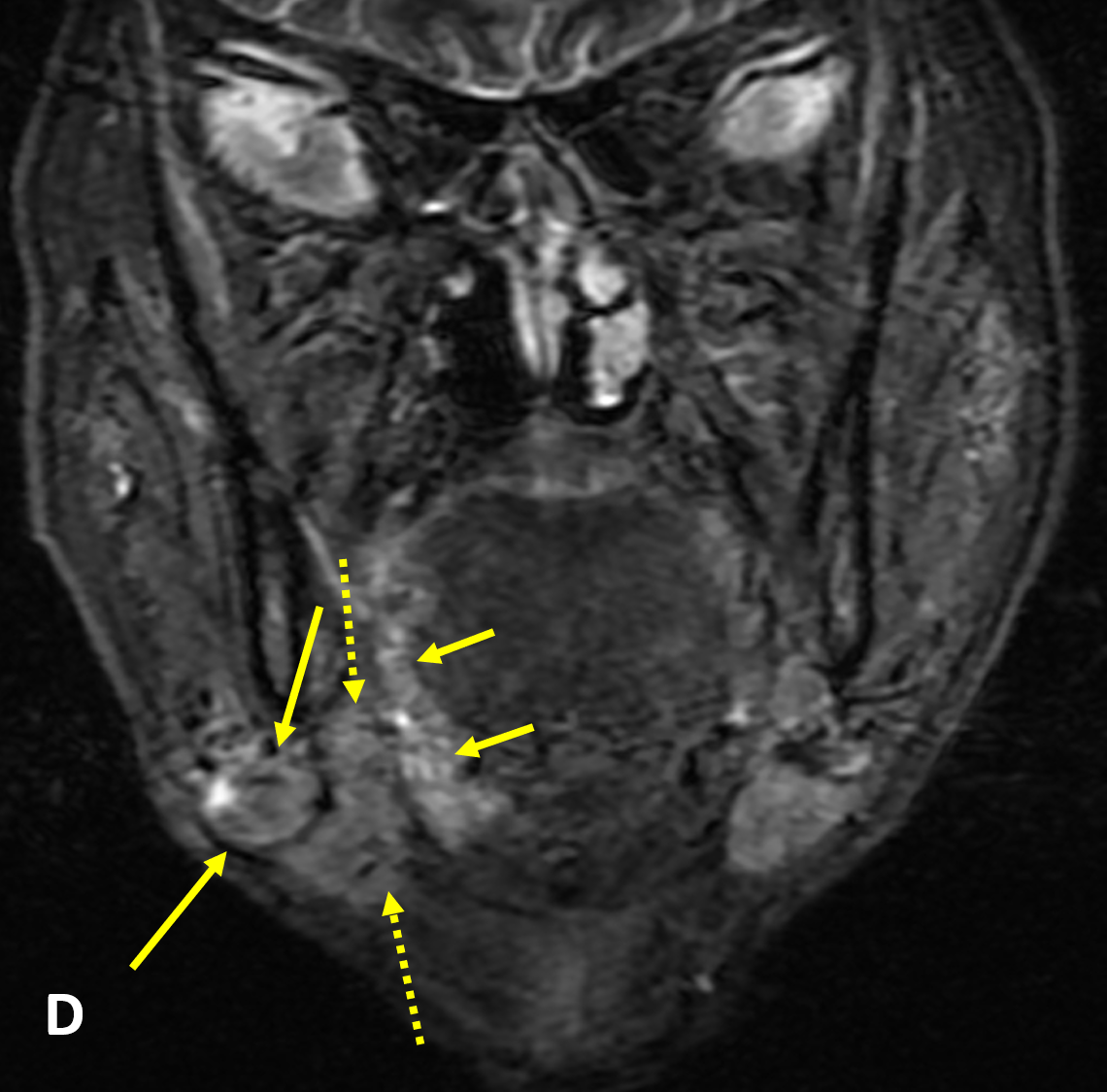
- SSCa of the tongue should be evaluated for 1) submucosal involvement, 2) involvement of the intrinsic muscles of the tongue, 3) crossing of the midline, 4) invasion of the pre-epiglottic fat, 5) osseous involvement, 6) perineural spread, and 7) lymphadenopathy
- MRI is better than CT for characterizing the primary tumor and perineural spread due to less dental amalgam artifact and better soft tissue resolution
- Subtle cortical erosions are best detected with CT, whereas marrow involvement is best assessed with MRI
- MRI findings of osseous involvement on T1 imaging include loss of low signal cortex, marrow replacement with intermediate signal tumor, and tumor enhancement (on fat-suppressed sequences)
- Pathologic lymph nodes are round and enlarged (maximum longitudinally): >8 mm (retropharyngeal), >15 mm (jugulodigastric), and >10 mm all others; size criteria is decreased to 8-11 mm axially and if >3 enlarged nodes in same drainage area; poorly defined nodal margins and soft-tissue stranding around nodes indicates extracapsular spread
Pearls
- Nodal involvement is the single most important prognostic indicator of head and neck SCCa
- Evaluation of the midline of the tongue and the contralateral neurovascular bundle is important for surgical planning because any invasion of the midline precludes hemiglossectomy
References
- Trotta BM, Pease CS, Rasamny JkJ, Raghavan P, Mukherjee S. Oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell cancer: key imaging findings for staging and treatment. RadioGraphics. 2011; 31:339–354
Case-based learning.
Perfected.
Learn from world renowned radiologists anytime, anywhere and practice on real, high-yield cases with Medality membership.
- 100+ Mastery Series video courses
- 4,000+ High-yield cases with fully scrollable DICOMs
- 500+ Expert case reviews
- Unlimited CME & CPD hours